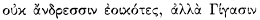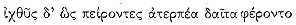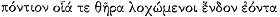A—
The Samothracian Mysteries and Passage to Oros Arkton (910–60)
Apollonius did not invent the detail regarding the Argonauts' stop at Samothrace. In his satyr play The Cabiri (cf. Athenæus 10.428f [= 95–97a Radt]), Æschylus portrays the Argonauts in a drunken celebration on the island. Moreover, Diodorus (4.43.1–2) recorded a tradition wherein the Argonauts were saved in a storm as a result of Orpheus's initiation into these rites. Apollonius's innovation would appear to be his integration of this detail of the Argonautic tradition in the episode involving Oros Arkton. Of particular note is the fact that the poet has so neatly associated the rites on Samothrace with those on Mount Dindymon through the structure of the episode and the several verbal correspondences noted
above. In addition to this, one can observe that certain mythological and legendary details regarding the Samothracian Mysteries parallel the events on Oros Arkton, which I shall examine below. I shall point out here instead that the manner in which Apollonius presents the two corresponding rites parallels the embassies of Æthalides and Iphinoë in the previous episode. There, Apollonius explicitly refused to mention Æthalides'
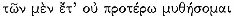
The rest of the first section contains an account of the journey from Samothrace to Oros Arkton and a brief description of the island-peninsula and its people. In describing the passage through the Hellespont, Apollonius has his eye on Homer's brief description of the area in the Iliadic Catalogue; in particular, for lines 928–35 the poet is indebted to Il. 2.819–43, about which Delage stated: "L'ordre suivi par Apollonius est à remarquer; il a énuméré toutes ces villes à leur place exacte, dans l'ordre où on les trouve en remontant l'Helléspont comme s'il avait eu sous les yeux une carte ou un périple. Il a donc complété en les précisant les renseignements que lui fournissait Homère."[16] In his adaptation of these Homeric verses the poet would appear to have gone beyond a mere updating of geographical details. We learn in the second and central section of the episode (B) that Cleite, the wife of Cyzicus, who will commit suicide after her husband's death, is the daughter of Merops of Percote:
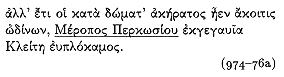
But still at home his wife, fair-haired Cleite,
offspring of Percosian Merops , had no experience
of the pains of labor.
[15] See Chapter 6, pp. 114–16.
[16] Delage 93.
Homer mentioned this same Percosian prince within the Iliadic passage that inspired Apollonius's description of the journey to Oros Arkton:[17]

These men were in the charge of Adrastus and Amphius of the
linen cuirass,
the two sons of Percosian Merops , a man who excelled all others
in the knowledge of prophecies and thus did not allow his sons
to go to war, the destroyer of men. Yet the two sons
did not obey, for the fates were leading them on toward black
death.
As we observe, Merops was the father of two other children in addition to Cleite, sons whose premature deaths in the Trojan War he had foreseen and in vain tried to prevent. Quite appropriately, then, he is also the father of Cleite, who married a man whose death in battle has been foreseen and who will herself die young. From this Iliadic model, Apollonius may well have conceived the idea of using a prophecy to motivate Cyzicus's welcome of the Argonauts, which tragically leads to his death.
Homeric references in the brief description of Oros Arkton in section A, which immediately follows the account of their journey there, similarly look forward to certain details of the narrative in section B. The first occurs in the identification of the island:

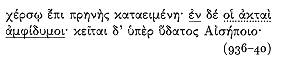
There is a steep island within the Propontis,
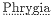
It lies out in the sea as far as its flooded isthmus stretches,
sloping toward the continent. On it are twin
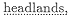
In this description, Apollonius has the following Odyssean passage in mind:[18]

There is a rocky island in the middle of the sea,
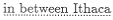
Asteris, not very large in size. On it are twin
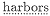
[sc. Telemachus].
Although the phrase
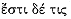
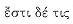
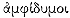
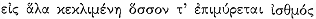
[18] Cf. Ardizzoni ad 936, Campbell ad 1.936ff.
[19] For an important discussion of the status of Cyzicus, see F. Vian, "L'isthme de Cyzique d'après Apollonios de Rhodes (1.936–941)," REG 91 (1978) 96–106.
isthmus. Silting was also responsible for connecting Cyzicus to the mainland in historical times.[20] In fact, there was a geographical controversy regarding the status of Cyzicus that went back at least to the fourth century B.C. : some held that Cyzicus was an island (Anaximenes of Lampsacus; cf. Strabo 14.635); others, that it was a peninsula with an isthmus (Scylax 94 GGM ).[21] Apollonius in typically Hellenistic fashion would seem to be responding to the disputed question by alluding to an answer; the imitation is Apollonius's erudite way of saying, "Cf. Asteris." And yet the reference is not purely academic. The context of the passage is germane to an important element of the Cyzicene episode: Asteris was also the place where the suitors set an ambush (
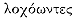
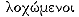
In the course of the episode, the Argonauts encounter both a hospitable and a hostile reception from the Doliones.[22] At first, when Cyzicus learns the identity of the Argonauts, he entertains them graciously. Later, however, when the wind blows them back during the night in their first attempt to leave the island, the young king leads an attack against the returning guests in the mistaken belief that they are enemies, the Pelasgian Macries. Apollonius sets the scene for this double reception with a subtle contaminatio of two Odyssean passages in the concluding lines of section
[20] See A. Philippson, "Reisen und Forschungen im westlichen Kleinasien," Petermanns Mitteilungen 167 (1910) 50ff., cited by Delage 97–98.
[21] For other ancient opinions that likewise were split over this issue, cf. Ruge, "Kyzikos," RE 12.1.295, who provides an intelligent discussion of the issue.
[22] A. R. Rose, "Three Narrative Themes in Apollonios' Bebrykian Episode (Argonautica 2.1–163)," WS 18 (1984) 117–18 (cf. Lawall 152, whom she cites in note 7), points out that in this respect, the present episode represents an inversion of the previous: the Lemnian women at first armed themselves for combat against the Argonauts and then, after receiving their embassy and after Hypsipyle spoke with Jason, welcomed them into their city; on Oros Arkton, the Doliones at first welcome the Argonauts and later, on their unexpected return, go to meet them in battle.
A that anticipate both hospitable and inhospitable receptions in Section B.
The first place where the Argonauts land is the port of Kalos Limen,[23] near which lies the Artacië Fountain, where the Argonauts will leave their anchor.[24] The phrase referring to this harbor recalls an Odyssean passage where the phrase
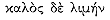

The port of Fair Harbor received the ship in its course.
There they removed the
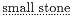
and, on the advice of Tiphys, they left it under a fountain,
the

that suited their needs. The Ionian Neleids years later,
in obedience to the oracle of Apollo, duly set up the first anchor
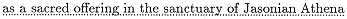

[24] The place where the Argonauts left their first anchor varies in some accounts: Callimachus locates it in Panormus, on the eastern side of the isthmus connecting Oros Arkton to the mainland (Ætia fr. 108 Pf.); Dionysius of Byzantium (87) set it at Ankyraion near the exit of the Bosporus, and Arrian (Periplus 9.2) at the mouth of the Phasis.
[25] Noted by Mooney, Ardizzoni, and Campbell ad 1.954, and Vian 261 ad 954.
A fair harbor lies on either side of the city
with a narrow entrance where curved ships
are docked; for there is a ship shed for all vessels.
Here there is also an agora near
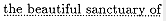
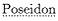
an area marked off by
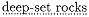
Apollonius not only borrows the phrase but appears also to have adapted an important detail of the Phæacian harbor, near which lay a sanctuary of Poseidon. For near the Cyzicene harbor the Ionians will build in time to come a sanctuary in honor of Jasonian Athena. We should also note a minor detail in which Apollonius seems to have inverted his model. The Phæacian sanctuary was located in the vicinity of the agora, where large quarried stones were sunk into the ground; conversely, the Argonauts leave their small anchor stone, which will eventually be dedicated in the sanctuary of Athena, at the Artacië Fountain.
This Odyssean passage comes from a speech of Nausicaa (ibid., 255–315) in which she offers to lead Odysseus to the house of Alcinous, her father. There he will eventually be welcomed and entertained. On the other hand, mention of the Artacië Fountain calls to mind another passage in the Odyssey where the exact opposite occurred:[26]

After disembarking, they [sc. Odysseus's men] went on a level
road, along which wagons
brought wood down from the lofty mountains to the city.
There before reaching the town they met a young girl fetching
water—
the virtuous daughter of the Læstrygonian Antiphates.
[26] Mooney, Ardizzoni, and Campbell ad 1.957 refer to this passage without comment on the possible relevance of the Homeric context to the Argonautic.
She had come down to the crystal-clear fountain,
In this passage, Odysseus's men meet the daughter of Antiphates, king of the Læstrygonians, also at an Artacië Fountain; like Nausicaa, the princess will lead them to her father's home. But rather than being welcomed and entertained, they are savagely killed and eaten by the cannibalistic Læstrygonians, who according to Homer resembled giants: