A
Ablabius (Novatian bp. of Nicaea), 73
Acacius (no. 1), 213 n. 55
Acilius Glabrio (no. 64): as advocate, 103 , 124 ;
as landowner, 102 ;
origins of, 101 , 462 ;
premature death of (before 360), 458 ;
succeeded to Ausonius's chair of grammar, 458 , 462
adaeratio, see commutation to cash of salaries in kind, 114 , 117 , 230
adventus of governor, teachers participate in, 123 , 154
Advocates: able to afford education, 25 ;
desired as bishops, 75 n. 182;
grammarians as, 103 -4, 124 , 131 ;
as representatives of literary culture, 92 ;
rhetoricians as, 105 ;
social mobility of, 28 , 124
Aelius Aristides: extraordinary immunities of, 226 n. 121;
use of 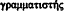 447
447
Aemilius Asper, 187 n. 47
Aetius (Arian theologian), 5 -6, 26 , 118 , 154 n. 59
Africa, teachers moving from, 126
Age rounding, as index of illiteracy, 35 -36
Agroecius (no. 181), 92 n. 309
Alexander (no. 4), 212 , 230
Alexandria, 106 , 126
alogus (critical sign), 191
Alypius (no. 6): called 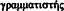 448 ;
448 ;
cured by Saint Thecla, 70
Amateurs: dedication of literary works by, 68 ;
relations of, with professionals, 35 , 53 -69 passim, 205 -10
"Ambrosiaster," 83
Ammonius (no. 9), 65 n. 137, 456 ;
as teacher of elementa , 462
Amphilochius (bp. of Iconium), 73
Analogy (analogia ): grammarian's use of, 172 -75, 207 ;
used to order the nature of the language, 177 . See also ratio
Anastasius (emperor), and Timotheus of Gaza, 125 , 202
Anastasius (no. 11), 456 , 457 -58
Anazarbus, grammarians at, 4 -6
Ancyra, 218 , 227
Annius Namptoius (no. 103), 111
annona (as unit of imperial salary), 116
Anonymus 1 (grammarian of Anazarbus: no. 167), 6 , 26 , 118 , 154 n. 59
Anonymus 3 (father of Calliopius: no. 169): as protégé of Libanius, 69 , 213 ;
status of, 108
Anthony, Saint, 21 -22
Antioch, 218 , 227 ;
chairs of rhetoric at, 455 ;
funding of teachers at, 107 , 115 , 218 ;
teachers attracted to, 126 -27
Antiptosis: and Nonius Marcellus, 186 n. 45;
Servius's conception and invocation of, 186 -87
antiqui. See Archaism; Authority (auctoritas ), of literary models; Classical authors
antiquitas , 171 ;
fusion of, with auctoritas , 185 ;
linguistic confusion in, 164 , 188 n. 52. See also Archaism; Authority (auctoritas ), of literary models; Classical authors
Antoninus Pius (emperor), 219 , 226
Apamea, 107
Aphraates (Syrian holy man), 79
Apollinarius (no. 14), 73
Apollonius of Tyana, 50
Appeal: to governor by teacher, 221 ;
legal, reference to one's education in, 23 , 42 . See also Petition to emperors
Approval (probatio , 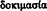 208 ;
208 ;
under Julian's school law, 216 -17
Archaism: contrasted with contemporary usage, 193 -94;
as deviation from natura , 183 -89;
grammarian's conception of, 182 -89;
produced by analogy, 172 -75. See also Authority (auctoritas ), of literary models; Classical authors
Arianism, of the Goths, 90
Arnobius: on the common language of Scripture, 83 ;
denying natural order of language, 85 , 176 n. 19
Ars (handbook): of Aelius Donatus, 139 -40, 148 ;
of Diomedes, 148 -49;
embodies rules derived by ratio from natura , 177 ;
of grammarian, 19 , 34 , 60 , 149 , 163 , 167 -68, 196 ;
regarded as dispensable by Augustine, 85 -86, 87 ;
relation of, to usus , 195 ;
of Remmius Palaemon, 53 ;
structure of, 140 ;
supposed etymology of, 34 , 163 . See also Pompeius, commentary of, on Ars of Donatus
artes necessariae , 224
Arusianus Messius, 174 n. 15
Assessor, former grammarian as, 124 -25, 131
Astyagius (no. 159), 141 n. 8, 149 Athanasius (Arian bishop of Anazarbus), 5 -6
Athanasius (dedicatee of Diomedes), 209
Athens, 106 ;
chairs of rhetoric and philosophy at, 217 ;
invitation to Libanius by, 222 -23;
number of chairs of rhetoric at, 455 -56;
removal of teachers at, 217 , 219
Attius Patera (son of Phoebicius), 102 , 209 n. 36, 457
auctores. See Archaism; Authority (auctoritas ), of literary models; Classical authors
auctoritas. See Authority
Aufidius Victorinus (son-in-law of Fronto), 223
Augustine (no. 20): at Cassiciacum, 86 ;
compared with Basil, 87 -88;
compared with Caesarius of Aries and Sidonius Apollinaris, 94 -95;
complains of delinquent students, 120 , 122 ;
De doctrina Christiana of, 84 -85;
education of, 21 , 24 , 25 , 28 , 103 ;
on education and ambition, 28 ;
family property of, 112 ;
grammarian viewed by, 17 , 84 -87, 206 ;
origins of, 24 ;
preaching style of, 83 -84;
and prestige of literary culture, 23 ;
as protégé of Romanianus, 212 -13, 230 ;
remained unmarried while teaching, 129 ;
as rhetorician turned bishop, 73 ;
on Rome's allure for teachers, 126 ;
secular career of, 106 , 129 , 222 , 230 ;
selfdiscipline of, 84
Ausonius (no. 21): as advocate, 103 , 124 ;
disagrees with Paulinus of Nola, 80 ;
early teaching of, 46 , 460 -61, 462 ;
education of, as indication of status, 103 ;
and Herculanus, 102 , 460 -61, 462 ;
as imperial tutor, 104 , 130 n. 167, 131 ;
landholdings of, 102 -3;
marriage of, 104 ;
mobility of, 28 , 100 , 104 , 129 , 130 -31, 462 ;
on movement of teachers from Bordeaux, 128 ;
origins of, 30 n. 83, 100 , 101 , 462 ;
as patron of Ursulus, 121 ;
as source for teachers of Bordeaux, 100 , 195 , 458 ;
succeeded as grammarian by Acilius Glabrio, 458 ;
tenure of, at Bordeaux, 456 -57, 458
Authority (auctoritas ): of God, and grammarian's rules, 195 ;
of grammarian, 55 , 86 , 164 , 169 -96 passim;
of literary models, 19 , 85 , 161 , 164 , 167 , 169 -96 passim;
secular and spiritual, relations between, 75 , 80 -95 passim. See also Status
Autodidact, 48 -49
Autonomy: of grammarian, 34 ;
limitations on, 64 -69;
of professional, 33 -34. See also Authority (auctoritas ), of grammarian; Differentiation
Autun, 116 n. 87, 218 , 227
Avienus (adulescens in Saturnalia ), 171 -72, 175 , 195