Porosity and Permeability
Although there is no direct relationship between porosity and permeability, both of these rock properties are extremely important when assessing the reservoir potential of a given rock type. Porosity in volcanic rocks is mainly defined by the abundance of vesicles. In the case of pyroclastic rocks, grain size distribution and sorting determine the packing density of clasts. The porosity of a pyroclastic rock generally imparts a primary permeability; if subjected to hydrothermal fluid circulation, this permeability may change as a result of the dissolution of glass and the growth of secondary minerals. As we said earlier in the section on density, the porosity of pyroclastic rocks may reach 80%, but for fresh, nonaltered pyroclastic rock, porosity is generally in the range of 40 to 60%. Lavas, on the other hand, exhibit porosity only if they are brecciated during emplacement or contain vesicles and other gas cavities such as lithophysae; in these cases, lava porosity is generally <20%.
The bulk permeability of volcanic rocks is a function of primary and secondary permeability. Primary permeability (sometimes called formation permeability ), as discussed above, develops from the original texture of the rock (for example, interconnected pores and vesicles and grain boundaries). In contrast, secondary permeability (sometimes called fracture permeability ) is promoted by rock fracture and foliation, and where it occurs, it is generally the dominant type of permeability. Volcanic rock fracture has numerous origins, such as tectonic movement and proximity to faults, differential compaction that causes stress fractures, cooling contractions, thermal spallation, and eruptive/emplacement brecciation. Typical permeabilities for all rock types range from 10-20 m2 (0.01 µDarcy) to 10-7 m2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
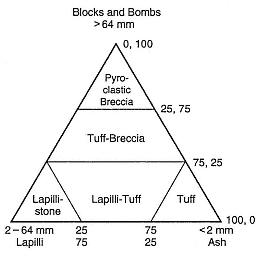
Fig. B.2
Classification scheme for pyroclastic samples
composed of a mixture of fragment sizes;
the term lapilli-tuff is
synonymous with lapillistone.
(Adapted from Schmid, 1981.)
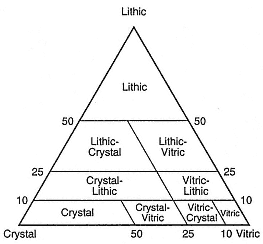
Fig. B.3
Classification scheme for pyroclastic samples
composed of a mixture of constituents.
(Adapted from Cook, 1965.)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(0.1 MDarcy), as shown in Table B.6. The permeabilities of unaltered pyroclastic rocks should be similar to those of silty and clean sand—in the range of 10-14 to 10-10 m2 (0.01 to 100.0 Darcy).