IX. Populations of the Sea
PLANT GROUPS OF THE SEA
In the sea, as on land, the plants are the real producers—that is, the organisms that are capable of elaborating complex organic substances from the simple inorganic compounds dissolved in the water. Without marine plants as synthesizers of primary food, development of marine animal life would be impossible beyond a negligible quantity that might be supported alongshore and in estuaries where particulate organic material of terrestrial origin would find its way into the sea.
A notable feature of marine vegetation is its dearth of variety when compared to the multiplicity of forms characterizing the terrestrial vegetation. Also, the types of plants most important in the production of primary food in the sea are in striking contrast to those constituting the chief synthesizers on land. This marked difference is readily explained, as we shall see, since it is dependent upon the radically different demands made on the plants by the marine environment. The poverty of plant variety in the sea is also in striking contrast to the abundant diversity of marine animal life. It may truly be said that the animal kingdom belongs mainly to the sea, while the terrestrial environment fosters the plants, although the most primitive of the plant groups, the algae, are wonderfully developed in the sea.
Light is of prime importance to all photosynthetic plants, and the possibility for attachment to the substratum is of secondary importance. More will be said about this later, but we must point out here that only in a very small portion of the sea are the two factors, light and suitable substratum for attachment, at the same time operative. This small portion of the sea wherein there may be sufficient light penetration to support attached plants—that is, the eulittoral zone—constitutes about 2 per cent of the sea floor.
Anyone frequenting the seashore is familiar with the covering of brown rockweed, Fucus, the green sea lettuce, Ulva, and a number of other low-growing plants that carpet the rocks in the intertidal zone. These or yet other relatively low-growing or encrusting plants may extend to varying depth below low tide if a suitable substratum for attachment is
The large kelps, such as Nereocystis, Pelagophycus, and Macrocystis, are found typically on rocky reefs some distance from the intertidal zone. Growth may occur on shoal reefs or rocks miles from shore, but the destructive mechanical effect of breaking waves and swells usually prevents any growth of these long-stiped forms in the immediate vicinity of exposed shores or rocks. Hence, the large kelps characteristically form in bands or patches some distance from shore where there is active circulation of water and yet where the danger of abrasion is reduced.
It was pointed out that only a small per cent of the sea floor may be considered to have sufficient light to support attached plants. Although this area may have enough light, it is vastly reduced as a suitable area for attachment of larger plants because of the great coastal stretches of mud, sand, shingle, or other unfavorable features. Therefore the bulk of the material produced by the attached marine plants is relatively small and can support only a small portion of the animal life actually present throughout the vast marine habitat; nevertheless, in more restricted areas along the coasts, attached plants—for example, the eel grasses—may be the chief producers. As a result of this restricted production by the benthic, or attached, plants, the primary food production becomes mainly a function of the unattached floating plants, notably, the diatoms and dinoflagellates, which, though microscopic in size, occur in vast, incalculable numbers.
Accordingly, our study of plant production must be concerned mainly with these floating forms. The means and adjustments by which this extensive community of floating plants—that is, the phytoplankton—is maintained and is related to other forms of life will be dealt with in subsequent chapters. First, however, in order to have a more complete understanding of the whole biological “setup” of the sea, it will be necessary as a point of departure to make a brief review of the various groups that are important to the economy of the sea as a whole.
The entire plant kingdom is divided into four primary divisions: the Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteredophyta, and Spermatophyta. Only the first and last of these are represented in the sea.
These primary divisions are each again divided and subdivided into many smaller secondary divisions which are indispensable to the specialist in marine botany, but for our purpose it will suffice to mention these smaller divisions only when they are important to marine economy, or when they have obtained rather widespread inclusion in more or less general literature dealing with the sea.
Only an abridged classification can be given. For a more complete treatment of the systematics the reader can refer to numerous good texts on botany or to publications dealing specifically with the group in which he is interested. A few of these publications are included in the bibliography, and yet others can be traced from those works included.
Thallophyta
Nearly all of the marine plants fall into this botanical division, which is made up of primitive plants in which the body shows little or no differentiation of vegetative organs—that is, no true root, stem, or leaf. Important among these thallus plants are the marine algae and the marine fungi, especially the bacteria. Since bacteria constitute the subject of a more specialized study of the sea, they will be dealt with under a special heading in chapter XVIII.
Most algae are beautifully colored, and sometimes also iridescent. The pigments of the chromatophores intercept solar energy, which is used in the synthesis of organic compounds. The type of pigment or pigment combination occurring in the algae as color manifestations has led to the names commonly used for the classes:
Blue-green algae (Myxophyceae)
Green algae (Chlorophyceae)
Brown algae (Phaeophyceae)
Red algae (Rhodophyceae)
Yellow-green algae (a heterogeneous group variously classified by different authors)
In general, the colors are characteristic of the classes, but other characteristics associated with cell structure and life history are more fundamental in distinguishing the five groups. Each group has a considerable variation in general morphology, some features of which will be pointed out in a review of the classes. The first four, with the exception of some blue-greens, are attached plants, while the yellow-greens are characteristically floating, or planktonic, forms.
Blue-Green Algae (Myxophyceae)
This class contains only small, poorly organized plants, some consisting of only a single cell, while others are multicellular. The blue color of these plants is due to a water-soluble accessory pigment, phycocyanin. In certain inland waters, it has been reported that upon the

Characteristic types of multicellular marine algae. a, Trichodesmium; b, Fucus; c, Alaria; d, Ulva; e, Ectocarpus; f, Sargassum; g, Rhodymenia; h, Polysiphonia; i, Cytosiphon; j, Lithothamnion.
Methods of Reproduction. Reproduction in this group is by asexual fission. This, the most simple method of propagation, consists of single individuals dividing to form two of lesser size, which in turn again divide after growth. In instances involving blue-green algae that form chains of cells, the chains divide into smaller sections known as hormogonia. Fission of the cells in the hormogonia again increases the length of the filaments.
Distribution. The Myxophyceae are of less general importance in the oceans than are the following algal groups. They are widely distributed in fresh and brackish water. In the sea they are most often found in the warmer waters, where they may cause the phenomenon of sliming. A brackish-water form, Nodularia spumigena, native to calm fjords of the north, may at times cause extensive sliming of the waters. In the Gulf of Bothnia, sliming due to this or similar forms may assume considerable proportions.
Green Algae (Chlorophyceae)
As the name indicates, the algae of this class are green in color. The pigments of the chloroplasts include the two types of chlorophyll, a and b, and the various carotinoids. The yellow and orange of the latter pigments are masked by the abundance of the green chlorophyll. In contrast to the chitinous cell wall of the blue-greens, these plants produce walls that are largely cellulose—a carbohydrate as opposed to the nitrogenous product, chitin. Some green algae of the sea—for example, Halimeda of the Siphonales—become incrusted with calcium carbonate, and thus may contribute materially in some places to the formation of lime deposits in warmer seas. The joints of the plant remain uncalcified, and thus allow flexibility in the moving water.
There is great diversity in the morphological features of this class. Common forms are filamentous with septa (Urospora) or without septa (Codium), tubular (Enteromorpha), and sheet-like (Ulva, or sea lettuce) (fig. 68d).
Methods of Reproduction. Common methods of reproduction may be illustrated by the habit of the cosmopolitan Ulva. In sexual reproduction the contents of any of the ordinary cells of the flat two-layered plant may form biciliated bodies called gametes which, upon escaping into the water, unite in pairs and by cellular division grow to form the new plant, known as the sporophyte, but usually passing first through a filamentous stage. Reproduction may also be asexual, in which case any of the common cells of the sporophyte plant may form microscopic quadriciliate zoospores (spores are simple reproductive cells which differ from seeds mainly in that they do not contain any ready-made embryo plant). These zoospores, upon being discharged, grow directly into gametophytes, the plants that produce the gametes.
During the period of reproduction, large swarms of gametes and zoospores may be released, leaving the parent plant colorless and forming a green “bloom” on the waters of quiet bays. For many filter-feeding animals, the floating microscopic reproductive products of these and other algae form a source of food that must not be overlooked in a study of food of littoral animals. In bays, also, these swimming stages of algae, as well as algal slime, contribute to primary film formation that leads to an eventual fouling growth on ships and other submerged structures.
Distribution of Green Algae in the Sea. The green algae are found mainly in the upper littoral zone, especially in the lower half of the tidal zone, and in the immediate subtidal region down to a depth of 10m or more, and therefore in a relatively well-lighted habitat. It is with the green algae that the fresh-water algae are most closely related.
In geographic distribution, green algae are found most abundantly in the warmer seas. Algologists have remarked on the relative scarcity and dwarfed development of the Chlorophyceae in the Arctic Sea.
Brown Algae (Phaeophyceae)
Brown algae belong almost entirely to the sea, only a very few occurring in fresh water. Here are included the conspicuous brown seaweeds, many of which grow to notably large size. The pigments of this class include green chlorophyll, which is masked by the yellow and brown pigments, xanthophyll, carotin, and fucoxanthin.
Plants of this class of algae form the conspicuous offshore growths popularly known as “kelp beds.” They are the giants among the seaweeds, and form the marine forests among whose waving stipes and fronds myriads of neritic fish obtain their food and seek shelter from their aquatic enemies. These, also, are the kelps commonly harvested in many places for the commercial products they yield.
The brown algae possess a great range of size and structure. There are minute, delicate, filamentous branching plants (Ectocarpus, fig. 68e); coarse, hollow, sausage-like chains a foot or more in length (Scytosiphon, fig. 68i); short-stalked forms with broad thalli (Laminaria, Costaria, and Alaria, fig. 68c, some of which become nearly 2 m broad); many branched forms (Fucus, Egregia); and long-stalked giants of the Pacific with long leathery fronds (Macrocystis, Nereocystis, Pelagophycus).
In structure the brown algae are the most advanced of all thallophytes. If we refer only to the more superficial details, Nereocystis
Nereocystis may attain a length of 35 m or more. The plant is anchored to a hard substratum by means of a profusely branched structure known as the holdfast, but there are no true roots. From the holdfast extends the long cylindrical stipe, which is hollow through most of its length and ends distally in a large hollow bulb. This bulb, like the stipe, is filled with gas, giving buoyancy to the plant. Ribbon-like fronds or laminae issue from the distal end of the bulb.
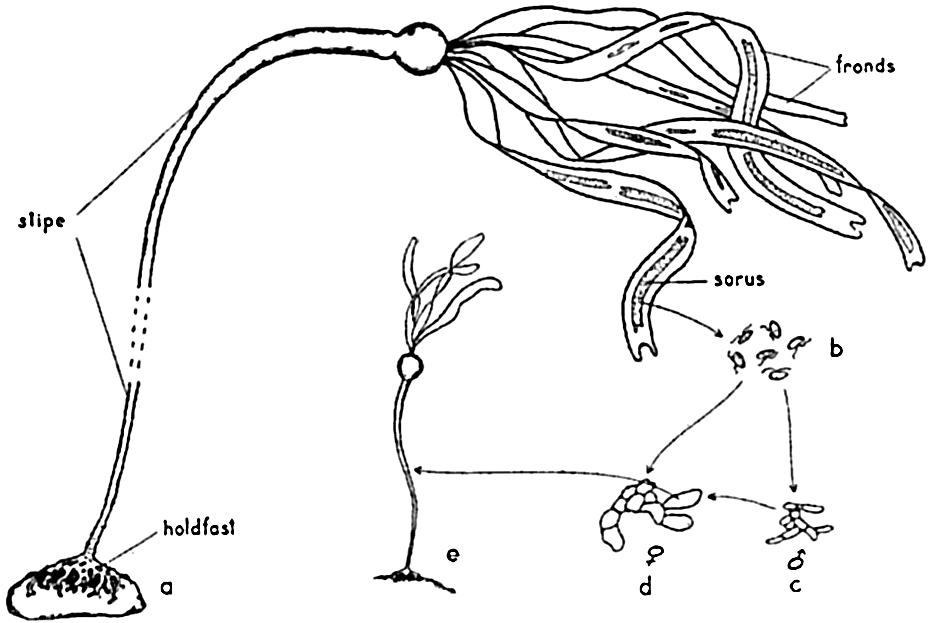
The gross structure and life cycle of Nereocystis. a, sporophyte plant; b, swimming zoospores; c, male and d, female gametophyte plants; e, young sporophyte.
The hollow bulb and stipe maintain the upper portion of the plant near the surface, exposing the fronds to favorable light conditions. In common with other large algae, the parts are tough, flexible, and slippery in order to withstand with least resistance the effect of frequently violent storm waves and strong currents.
Methods of Reproduction. The life cycle of the brown algae includes various types of alternation of generations. Commonly, in the Laminariales, which includes the large kelps, there is an alternation of generations that may be illustrated by the cycle shown in Nereocystis (fig. 69). Here the large, conspicuous sporophyte plant produces a series of sori, or “fruiting areas,” appearing as dark brown patches running longitudinally along the whole length of the fronds. Beginning at the distal end of the frond, these patches are detached at maturity, leaving a broad gap (3 to 10 cm) in the frond. From the mature sori, innumerable ciliated zoospores escape and, upon reaching a suitable substratum, grow to small filamentous plants, the inconspicuous gametophyte stage. Thus the alternation of generations in this form is
In the brown algal group, Fucales, to which Fucus and Sargassum (fig. 68f) belong, the main plant is a sporophyte, but, within the thousands of tiny cup-like conceptacles forming the bladders, gametes are formed like spores. These unite after being discharged free in the water. Thus the alternation of generations is evident only cytologically. In connection with the “spawning” of Fucus, it is interesting to note that it is rhythmic with the tide, taking place after a period of exposure at low tide.
Distribution. The brown algae reach their maximum development in cooler waters, and are therefore typical of the rocky coast of higher latitudes. Sargassum and others of the Fucales are characteristic, however, of tropical or subtropical regions. Tilden (1935) is of the opinion that the Laminariales arose in the North Pacific, while the Fucales had their origin in the South Pacific. Several species or varieties of Sargassum, or “gulfweed,” are found in large quantities in the Sargasso Sea, whence they have drifted and multiplied after being torn loose from coastal areas. They are kept afloat by air bladders and grow vegetatively, propagating by fragmentation, but apparently do not form fruiting bodies. The drifting masses form a characteristic environment with associations including other algal and animal forms of littoral type.
The vertical distribution of brown algae shows many low-growing forms, especially the Fucales, in the rocky intertidal zone. Near the lowest tide level the medium-sized forms with leathery fronds and short limber stipes begin to prevail, and they increase markedly in the next 15 to 20 m of depth, finally diminishing and disappearing below the eulittoral zone.
Intermingled with these short-stiped algae are the giant long-stiped kelps that usually grow most abundantly some distance from the shore and extend to depths of 30 m or more. Macrocystis, one of the giant kelps of the Pacific, is said to reach to the surface from a depth of 80 m off the coast of Chile (Hesse, Allee, and Schmidt, 1937), but in the North Pacific it has its most abundant growth in water of about 15 m. Kelps of this genus are said to be absent from strictly tropical waters and, as a
Mention should also be made of epiphytic forms such as the filamentous Ectocarpus (fig. 68e), which prefers to be attached to other algae growing at various depths.
Red Algae (Rhodophyceae)
Nearly all of the red algae are marine. From the standpoint of color, they are the most striking of all the marine algae, some of them being also highly iridescent. Many of the delicate forms are among the most beautiful macroscopic objects of the sea. The order Gelidiaceae ranks first in importance commercially since certain of its members form the main source of agar.
The pigments of the chromatophores include the usual chlorophylls together with xanthophyll, carotin, and, in addition, the red phycoerythrin and sometimes phycocyanin. The plants may appear red, purple, violet, or, to some degree, brown or green. The deeper-growing species are the more purely red, a fact which is perhaps associated with their ability to synthesize more efficiently in the subdued light of greater depths than are the shallow-water types (Gail, 1922).
Though usually small in size, the red algae show a diversity of form much greater than the brown, and they are also more numerous. All are multicellular, the simplest being filamentous branching forms like Polysiphonia (fig. 68h), which, together with other filamentous algae, are commonly called “sea moss.” The larger flat types may be illustrated by Rhodymenia (fig. 68g), in which the broad frond may attain a considerable length. However, the maximum length of the larger red algae is only about 1 to 2 m.
Methods of Reproduction. The life cycle of some species is very complicated and cannot be amply discussed here. The reader is referred to the works of Kylin and other texts for a more complete treatment. In the higher types there is a regular morphological alternation of generations in which the sporophyte and gametophyte may superficially appear similar. Polysiphonia is commonly used to illustrate the life cycle of red algae. Here three types of plants are produced—namely, a male and a female gametophyte and an asexual tetrasporic plant. The last arises from the carpospores, which occur on the female plant. The carpospores are the products of union of male and female gametes. Upon germination, the tetraspores of the asexual plant give rise, in turn, to the sexual plants.
One of the most remarkable features of reproduction in red algae however, is the complete absence of any ciliated or flagellated swimming spores or gametes. This feature is a notable departure from the rule
Distribution. The Rhodophyceae are widely distributed geographically, but are most abundant in temperate seas. Their vertical distribution indicates that they prefer to grow in subdued light. A few species may be found in the intertidal zone, but the most luxuriant growth is subtidal. They may occur in abundance in depths less favorable to most of the green and the brown algae, and in the Mediterranean they have been reported from depths of 130 m. Thus, from shallow to deep water the general vertical distribution of the algal groups discussed is successively the green, the brown, and the red, with a wide degree of overlapping.
It should be mentioned here that certain red algae (the Nullipores) play an important role in calcium carbonate precipitation in the sea. They have contributed, and still do contribute, greatly to geological formations. Among these are, especially, the coralline algae, of which Lithothamnion (fig. 68i) is a typical example. They are distributed from lat. 73°5′ S to 79°56′ N (Tilden, 1935) and can be observed as copious encrustations on rocks and shells in the littoral zone of every exposed shore.
Yellow-Green Algae
There is considerable disagreement as to the proper grouping and status of divisions within this heterogeneous assemblage of organisms, some of which, as indicated below, are animal in nature. As a matter of convenience in discussing the more important marine members, we shall here employ only names of more or less familiar usage in biology and oceanography. Many of the members included are classified as animals in zoological texts, but in consideration of their holophytic nature (faculties of photosynthesis) it is most convenient for oceanographic studies to include them a priori among the producers. For more detailed treatment of the systematics of the various divisions, the reader is referred to Fritsch (1935) and the relevant works included in the discussions under the separate groups.
In contrast to the algae previously discussed, the members of this assemblage of plants and plantlike animals are primarily floating forms and will be taken up in the order of their importance in the economy of the sea.
Diatoms. The plants here included are all microscopic in size, the larger species viewed individually appearing only as tiny points. Some earlier authors of marine botany included them with the brown algae. A comprehensive treatment of the group is given by Hustedt (1930). In structure they are unicellular, but individuals may form chains or groups of various types. Examples of types representing the common genera are
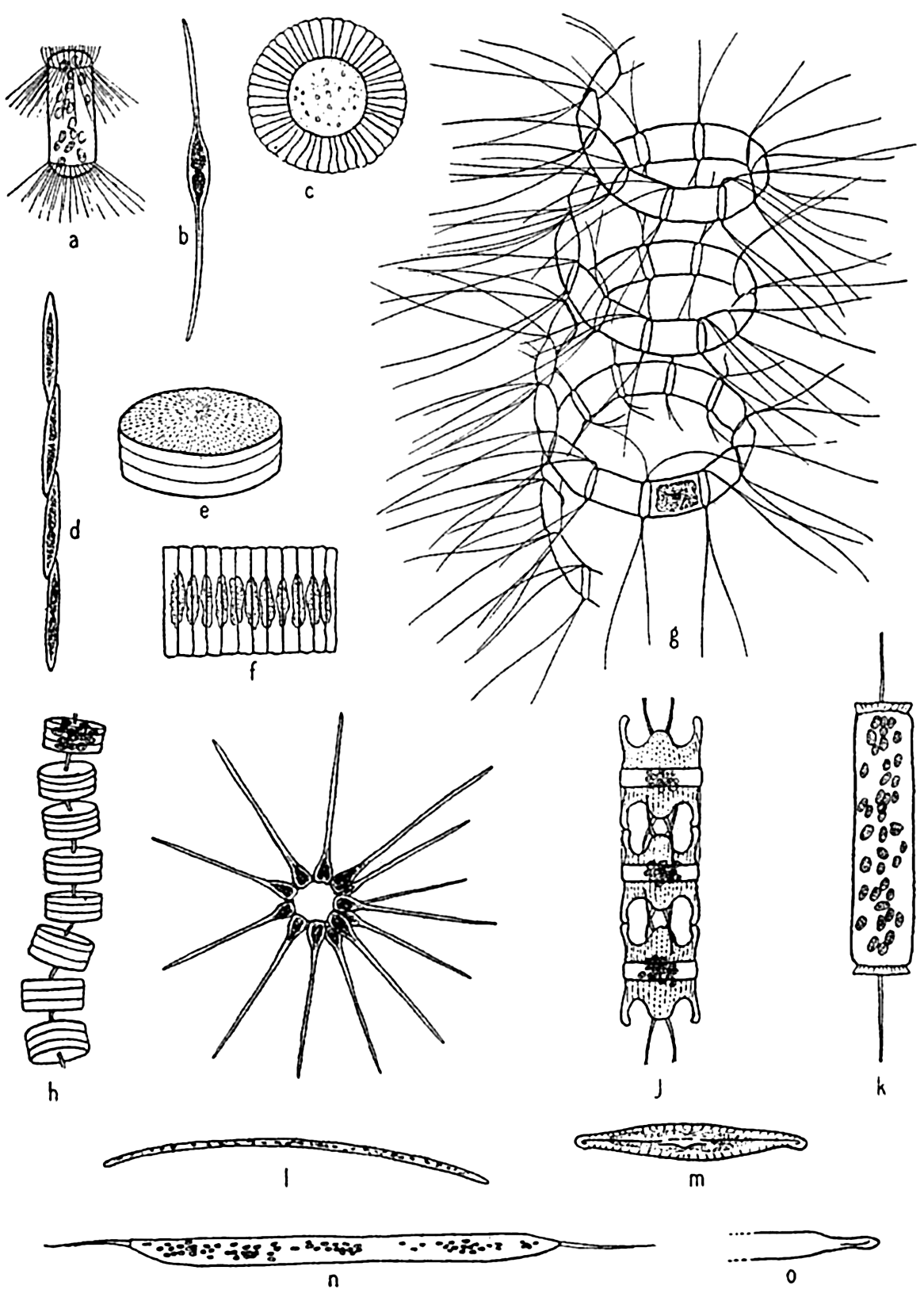
Characteristic types of diatoms. a, Corethron; b, Nitzschia closterium; c, Planktoniella; e, Coscinodiscus; f, Fragilaria; g, Chaetoceros; h, Thalassiosira; i, Asterionella; j, Biddulphia; k, Ditylum, l, Thalassiothrix; m, Navicula; n, o, Rhizosolenia semispina, summer and winter forms.
Since these plants as a group may be considered the most important in the economy of the sea, it is imperative that we treat them in considerable
The shell structure of diatoms (fig. 71) may be likened to a box with a telescoping lid, because it consists of two nearly equal halves fitted one over the other. The pieces corresponding to the top and bottom of the box are known as the valves, and these are each joined by connecting bands that overlap and together form the girdle. The larger half of the shell is known as the epitheca, and the smaller half, which fits into it, as the hypotheca. The protoplasm lies wholly within the shell, but for exchange of metabolic products it is exposed by a slit (raphae) in the valve of some types and by small pores in others.

The gross structure of a simple diatom (Coscinodiscus). a, valvular view; b, girdle-view section of cell wall.
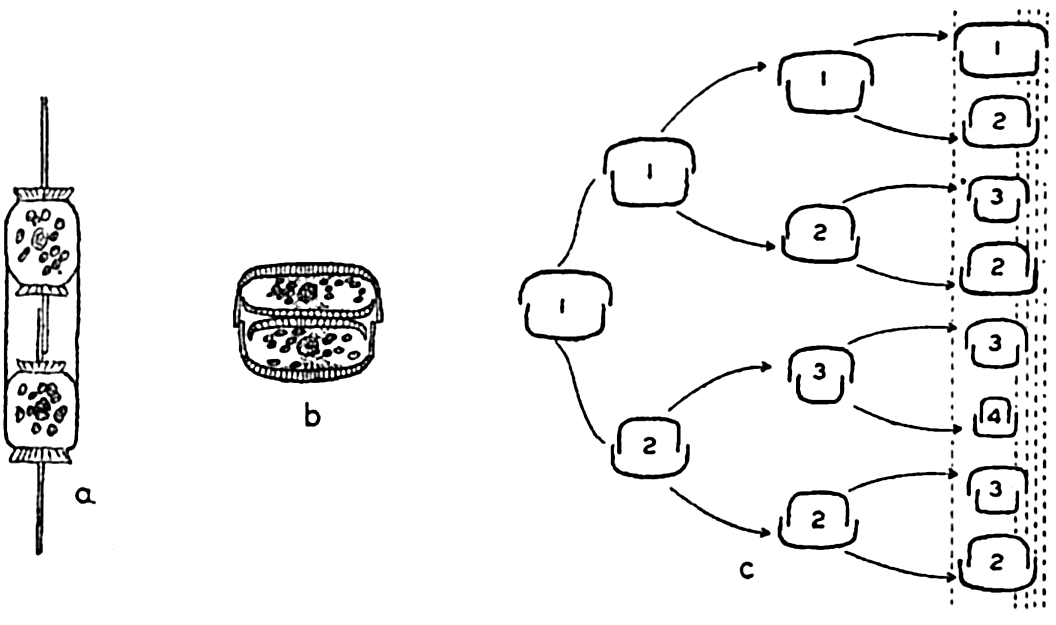
Reproduction in diatoms. a,b, cell division; c, diminution of size resulting from cell division in three generations.
Diatoms may possess only one or many chromatophores, which may vary in color from yellow to olive-green or brown. Authorities are in poor agreement as to the nature of the pigments present, but there is some indication that the common pigments are masked by the accessory brown pigment diatomin, which may be identical with fucoxanthin of the brown algae. An important product of assimilation is an oil that is frequently visible as droplets within the diatom.
Methods of Reproduction. The most common method of propagation among the diatoms is by simple cell division (fig. 72a). This method has a far-reaching effect on the population in two distinct ways. First, it is conducive to a rapid production of enormous numbers when
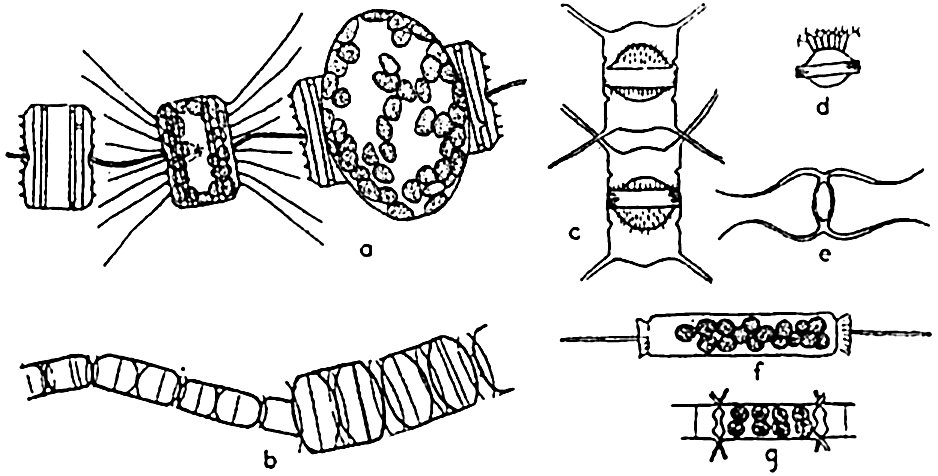
Reproduction in diatoms. a, auxospore formation in Thalassiosira aestivalis (after Gran and Angst); b, increase in cell size following auxospore formation in Melosira nummuloides (after Fritsch); c, resting spores in mother cells, Chaetoceros vanhurckii; d, resting spore of Chaetoceros diatema; e, resting spore of Chaetoceros radicans; f, microspores in Ditylum; g, microspores in Chaetoceros didymus (after Gran and Angst).
Diatoms may also produce what are known as microspores (fig. 73b). These were early observed by Murray, Gran, and others. They consist of small protoplasmic spheres occupying the shell, and may escape as biciliated spores. The significance of these bodies is not fully known.
Resting spores of characteristic structure (fig. 73c) are also formed in most pelagic neritic species, especially of the centric types, by the cell contents becoming condensed and surrounded by a heavy, siliceous wall. They may be produced at the initial appearance of unfavorable living conditions, and may drift for some time within the old frustule or sink to the bottom to survive the unfavorable seasons of inadequate nutrients, cold, or of varying salinity so characteristic of many coastal areas. Gran (1912) has reported them from Arctic collections in which they were enclosed in ice.
Winter and summer forms of oceanic diatom species have been reported. These are cases of marked dimorphism in which the coarse winter forms have been looked upon as a means of survival from one favorable season to another. However, the dimorphism may be only an adjustment to changes of viscosity inherent with seasonal temperature changes.
Many diatoms grow normally on the bottom in the littoral zone, where they may or may not be attached by stalks or glide freely over the bottom. These benthic forms produce the heavily shelled types with most exquisite designs. Diatoms may also grow in profusion on other plants and animals. The littoral genus Licmophora frequently occurs on pelagic copepods, and the massed growth of Cocconeis ceticola flourishing on the skin of whales that have spent considerable time in the cold antarctic waters has, by its yellow color, given rise to the name “sulphur-bottom” for the blue whale.
Dinoflagellata. These are frequently spoken of collectively as the dinoflagellates (fig. 74). Space will not permit the amount of discussion that this diverse group of organisms requires for adequate treatment (see Kofoid and Swezy, 1921, Kofoid and Skogsberg, 1928, Fritsch, 1935). It is a group concerning which it is not easy to make generalizations without the danger of introducing errors. The members are of great importance in the economy of the sea. A large number are holophytic and rank second to the diatoms as producers in the marine plankton. They are therefore best studied with the phytoplankton. Others are holozoic or animal-like in nutritional requirements, ingesting particulate food and possessing other characteristics that place them clearly with the animals. Some are saprophytic, living upon dead organic matter. All are important as food to filter- and detritus-feeding animals.
Typically, the dinoflagellates are unicellular, some being armored with plates of cellulose, others unarmored or naked. All possess two flagella for locomotion, an important feature in the holophytic forms, for
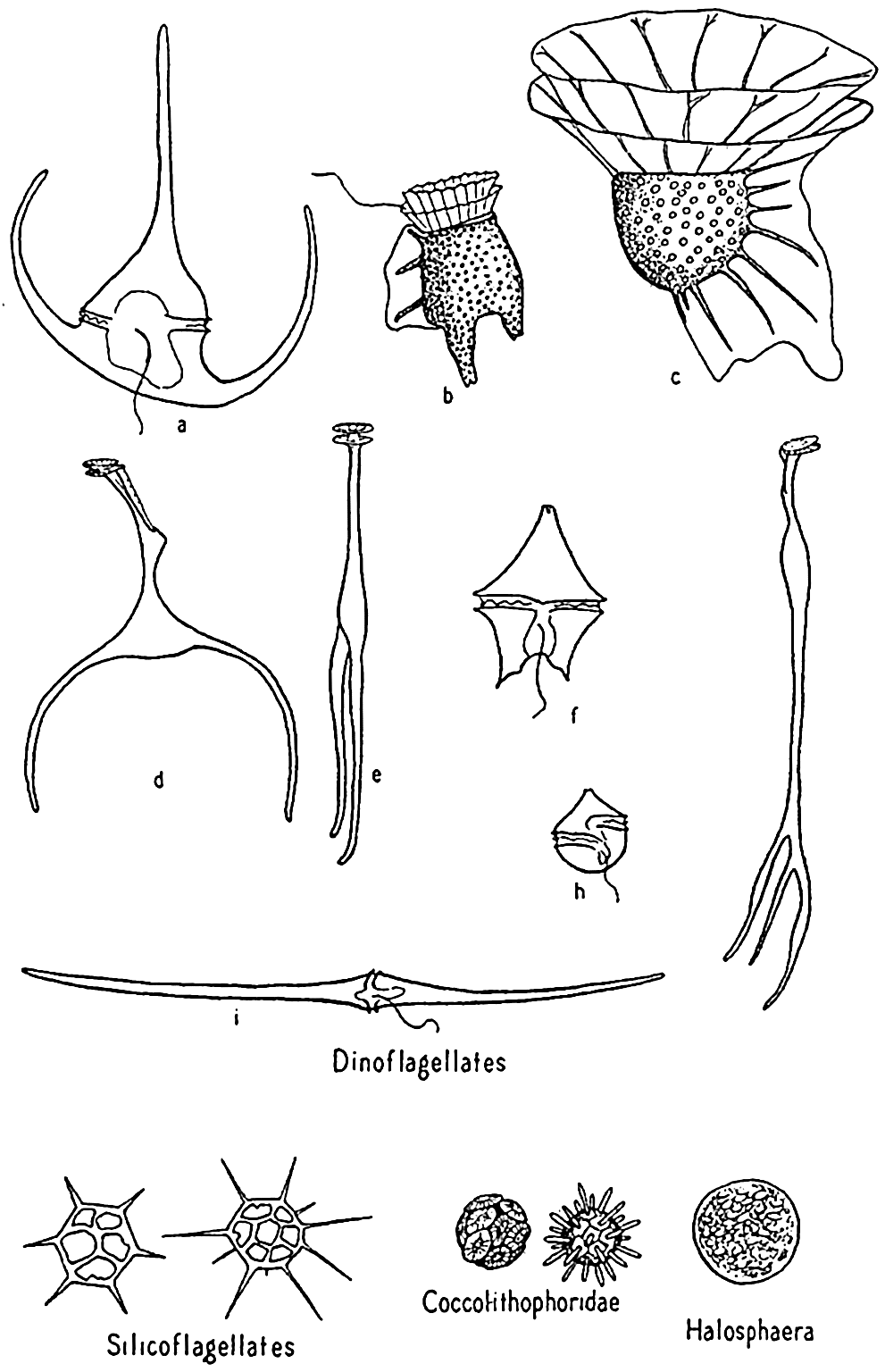
Dinoflagellates and other phytoplankton organisms. a, Ceratium tripos; b, Dinophysis; c, Ornithocercus; d,e, Triposolenia, front and side views; f, Peridinium; g, Amphisolenia; h, Goniaulax; i, Ceratium fusus.
Methods of Reproduction. Among the dinoflagellates, reproduction is accomplished mainly by processes of cell division, which in some instances result in a chain of individuals clinging loosely together. Temporary structural variations may normally occur in individual cells at opposite ends of the chain. The progressive size reduction that is
Dinoflagellates are found in all seas, but the greatest development of species is met with in the warmer waters, where a number of very bizarre forms are to be found. Owing to the destructibility of their cellulose plates by bacteria and other agencies, they are not preserved in bottom deposits. Important genera are Ceratium, Peridinium, Dinophysis, Gonyaulax.
Phaeocystis. Phaeocystis is a brown, flagellated plant, neritic in habit, that forms colonies in gelatinous, lobed globules visible to the naked eye. The large numbers produced may at times render the surface water quite brown and become a serious cause of clogging in silk plankton nets. Reproduction is accomplished by formation of flagellated spores that escape from the colonies.
Coccolithophoridae. Among the smallest (5 to 20 microns) of autotropic organisms of the sea are the biflagellated (some marine forms are not flagellated) forms of this group (fig. 74). Usually they are not caught by the ordinary net, through the meshes of which they readily escape, and when caught special care must be taken that their calcareous protecting armor is not dissolved by the preservative, leaving only an indefinable mass. The soft parts are shielded by tiny calcified circular plates or shields of various design and projections called coccoliths, or rhabdoliths. These shields had been found in enormous numbers in marine bottom deposits before the organisms of which they are a part were discovered by the Challenger and identified from their living habitat in the plankton, where they were found entangled in protoplasmic strands of pelagic protozoa or in the stomachs of salps and pteropods. Typically, the coccolithophoridae belong to the open sea, but they may occasionally reproduce in large numbers in coastal waters; at one time, according to Gran (1912) numbers of 5 to 6 million per liter gave the waters of Oslo Fjord a milky appearance. Some also occur in fresh water.
Though minute in size, they are of great importance as food to filter-feeding organisms, and also as contributors to calcareous bottom sediments. They occur in geological formations dating from the Cambrian period. Common genera among these organisms are Coccolithus, Pontasphaera, and Rhabdosphaera.
Halosphaera. Halosphaera is a unicellular, microscopic plant of the order Heterococcales (fig. 74). Earlier authors have included it with the green algae. It occurs at times in vast numbers in the plankton, floating mostly near the surface. Halosphaera virides occurs over the whole Atlantic and is abundant both in the warmer waters of the Gulf Stream system and in high southerly latitudes, where the Discovery investigations in the Antarctic found it second in importance to the diatoms. Meringosphaera of this order also occurs in marine plankton.
According to Gran, Halosphaera is practically the only open-sea form in which the predominantly green color of land plants is to be found. Notwithstanding the vast numbers that are often found, it does not reproduce by the quick method of simple binary fission, as in diatoms, but, after having grown for some time to its maximum size, the cell contents are transformed into a large number of zoospores. These swimming spores escape and through some unknown method are transformed back into tiny globular forms that gradually increase to normal size by successively shedding their weakly silicified investing membranes. Resting spores may also be produced.
Silicoflagellates. These flagellate organisms (fig. 74) deserve mention only briefly, since they do not usually occur in sufficiently large numbers to enter materially into the economy of the sea. However, they are such persistent members of plankton communities from nearly all colder seas that their starlike, open, siliceous shells attract a good deal of interest. Many occur in bottom sediments, and their development is shown in fossil marine deposits. That they contribute at least in a small way to the food of animals is shown by their frequent occurrence in food vacuoles of tintinnids.
The Higher Plants in the Sea
The two intermediate phyla of the plant kingdom—namely, the mosses (Bryophyta) and the ferns (Pteridophyta)—are wanting in the sea. However, the highest of plants, the Spermatophyta, are represented by about thirty species of Angiosperms, or flowering plants. These belong to three genera of the Hydrocharitaceae and six genera of the Potamogetonaceae (Arber, 1920). They have not originated in the sea, but have invaded and colonized it by way of fresh water. Their closest affinities are with widespread fresh-water angiosperms belonging to the same families.
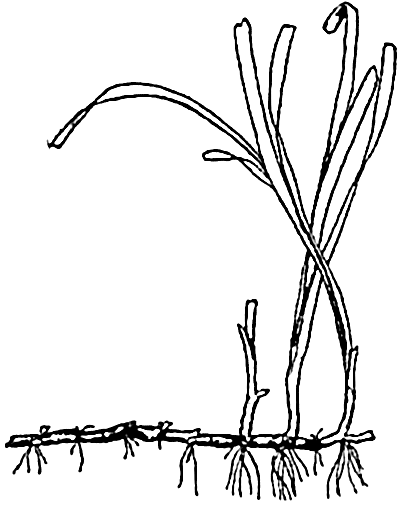
The eel grass Zostera, to show leaves, rhizome, and true roots.
Of outstanding importance among the marine angiosperms is the eel grass, Zostera (fig. 75). Botanically, the plant is not a grass despite the long, slender, and flexible grasslike leaves, which are thus adapted to withstand the force of moving water. Unlike the benthic algae, Zostera and its relatives possess true roots that are attached to an underground stem, or rhizome, forming an anchor in the soft substratum. There are fertile and sterile plants, and, since the plants grow submerged, mostly in depths of 4 or 5 m but also to a depth of 14 m (Petersen, 1918), the flowers are pollinated under water through the agency of currents.
THE ANIMAL POPULATION OF THE SEA
Many different species of distinct animal groups live intermingled in the same faunal area. Some may have identical habits and requirements, but for the most part the separate species or higher ranks have characteristic limitations, and each has its own function in conditioning the whole complex organic environment, thus influencing the type of species forming the association. This will become increasingly clear in considering the interrelations of the organisms (chapter XVIII).
For an adequate understanding of the intricacies of the fauna, it becomes necessary, therefore, to understand the part played by the separate species or groups of species, and, in order to circumscribe and to interpret the geographic and bathymetric distribution of species, their exact identity must be established. Systematic biology—that is, taxonomy—provides the tools for these purposes and is therefore an indispensable aid toward the desired goal. The field of study is so overwhelmingly large, however, that the many species comprising the primary groups must be investigated in special studies and the results of many different specialists must be integrated to provide a picture of the fauna as a whole. Much still remains to be done in this field, for many sections of the oceans have been only superficially investigated.
A full descriptive treatment of the animals of the sea would require several volumes, but it will suffice for our purpose to list or succinctly to review the primary divisions, including only a few of the secondary divisions that in the development of the study of marine biology and oceanography have assumed more or less importance and that are illustrative of the general field.
In the following synopsis, where the number of species is recorded for any group, the figures have been obtained mainly from Pratt (1935) and Hyman (1940). Illustrations are found mainly in chapter XVII.
Synopsis of the More Important Systematic Groups of Marine Animals
A. INVERTEBRATES
PHYLUM PROTOZOA
Protozoa are single-celled organisms microscopic or minute in size. The sea bottom harbors many creeping and attached protozoa of the ameboid or ciliate types, but we shall be concerned mainly with the pelagic forms inhabiting the plankton.
CLASS MASTIGOPHORA
Order Dinoflagellata. In the broadest sense, this group contains both animals and plants, it being a borderline group.
Foremost among the protozoa in the economy of the sea are the dinoflagellates, chiefly because of the capacity of many types to carry on photosynthesis. These holophytic members are considered more fully in the discussion on plants, and for oceanographic studies are properly included in the phytoplankton. It will suffice to mention here only Noctiluca (fig. 225g) as an important representative of the holozoic members, none of which have chromatophores. The soft spherical body of Noctiluca is pale pink in color and bears a conspicuous flexible tentacle. The maximum size is only about 1.5 mm, but, when reproducing in profusion by simple cell division, the countless numbers produced may, by their accumulation, impart a pinkish-red color to considerable areas of surface coastal water, and the masses may be blown into conspicuous windrows or patches resembling “tomato soup.” Noctiluca are voracious feeders, engulfing particulate food such as diatoms and other small organisms. This form is also important as a contributor to the luminescence of the sea.
CLASS SARCODINA
Order Foraminifera. The oceanographic interest of this order (and also, to some extent, of the following order) lies in the skeletal structures produced by its members. In the foraminifera the shells are variously formed, with one or more chambers arranged in a straight line or in a spiral (fig. 225a). Some are provided with many pores for the projection of protoplasmic pseudopodia used in capturing food. The shells are constructed typically of calcium carbonate, but silica and chitin are also used, and in some
Order Radiolaria. These are planktonic organisms whose skeletons are composed mainly of silica, but the Acantharia contain acanthin (strontium sulphate), and all types possess an inner capsule of chitin. The siliceous skeletons are formed in the most intricate and widely divergent patterns in the different species and are the most beautiful of all objects found in the sea (fig. 225e,f). Upon sinking and mingling with the bottom sediments, the skeletons become the type constituents of the siliceous radiolarian oozes found most abundantly covering the ocean floor in the deep tropical waters of the Pacific Ocean (fig. 253). There are about 4400 species, all marine.
CLASS CILIATA
Suborder Tintinnoinea. These protozoans, commonly called tintinnids, are mostly of extremely small size, varying from 20 μ for Tintinnopsis nana to 640 μ for Cymatocylis robusta. Swimming is accomplished by the beating of a whorl of hairlike cilia at the anterior end. Their loricae, or shells, range in shape from tubular to urn-shaped structures that are secreted in a stereotyped fashion by the animal and may or may not include agglomerated foreign material such as bits of sand, diatom shells, and coccoliths (fig. 225c,d). The tintinnids at times are found in vast numbers, especially in coastal water, where they are important feeders on the smallest plankton, the nannoplankton. Their sensitivity to small changes in environmental conditions makes them fluctuate in numbers with seasonal or other changes. There are 692 known species,
PHYLUM PORIFERA
The sponges are multicellular animals, though of simple and loose organization, either with spicules of silica or calcium carbonate imbedded in their bodies for support or with fibrous skeletons made of the horny substance spongin, as in the common commercial sponge. Sponges are all benthic and nearly all marine, only one family occurring in fresh water. In the sea they are to be found in all parts and at all depths, the siliceous forms living largely in the deep sea. Sponges grow attached to the substratum and obtain their food by propelling water through tiny pores in the body wall and filtering out the microorganisms and detritus that may be present. There are about 2500 species, mostly marine.
PHYLUM COELENTERATA
Coelenterata are tubelike primitive forms with a continuous body wall surrounding a simple digestive cavity with but one opening encircled by tentacles used in capturing food. The group shows a remarkable degree of polymorphism; that is, a single species may present a variety of forms reducible either to the sessile polyp or the swimming medusoid type.
Class Hydrozoa. To this class belong the hydroids commonly found growing in little tufts on rocks and sea weeds along the coast. From these branching polyps are budded the small jellyfish or medusae such as Obelia (fig. 79). The Siphonophora, an order of this class, are characteristic of the open sea and are represented by the beautiful blue Velella (“by-the-wind sailer”) (fig. 226b) and Physalia (the “Portuguese man-of-war”), neither of which possesses a sessile stage. They are planktonic colonial medusae, exhibiting the maximum development of polymorphism of all animals. There are about 2700 species of hydrozoa.
Class Scyphozoa. To this class belong the larger medusae with eight notches in the margin of the bell. Here are included the giant jellyfishes, some of which may become 2 m in diameter. A much-suppressed sessile polyp stage is present in the group. The 200 species are entirely marine. Examples: Aurelia, Cyanea.
Class Anthozoa. To this class belong the sea anemones, corals, and alcyonarians. There is no medusoid stage, and many of the polyps are colonial; some, especially the corals, are notable for their precipitation of calcareous skeletal structures, which, through long periods of accumulation, are important in the
― 307 ―building up of coral reefs and similar formations. All 6100 known species of anthozoa are marine.
PHYLUM CTENOPHORA
Ctenophora are small globular or flattened forms of jellylike consistency and with eight meridional rows of fused cilia used in swimming. Some possess a pair of trailing tentacles used in the capturing of food. The abundant globular species are commonly known as “comb jellies” or “sea walnuts” (fig. 226a). There are 80 species, all marine. Numerically important genera are Pleurobrachia and Beroë.
PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES
Platyhelminthes are flatworms, a large number of which are found in the sea, either free-living or parasitic.
Class Turbellaria. Nearly all of this class are free-living on the bottom under stones and in crevices, where they move about by means of cilia covering the body.
Class Nemertinea. These are ribbonlike worms sometimes considered as a separate phylum. The benthic species live among rocks, algae, mussels, and so on, or burrow in the bottom, where they capture small organisms by means of a long eversible proboscis. Extraordinary size variations occur, some species being only 5 mm long, while one, Lineus longissimus, may become 25 m in length when extended, and therefore is the longest of the invertebrates; however, its threadlike form contains but little bulk. Fifty-two planktonic species of nemerteans are known, some living at great depths—for example, Pelagonemertes. (Coe, 1926). The planktonic forms are modified, some with caudal and horizontal fins for swimming (fig. 228c). There are about 550 species of nemerteans, of which nearly all are marine.
PHYLUM NEMATHELMINTHES
The thread or round worms occur largely as parasites, but some are found in the plankton, and very large numbers occur in decaying organic detritus on the bottom. There are about 1500 species, many of which are nonmarine.
PHYLUM TROCHELMINTHES
Class Rotatoria (Rotifera). These are tiny benthic or planktonic organisms provided with rings of cilia for swimming and for gathering food. Vast numbers may occur in the neritic plankton during the warmer seasons. There are about 1200 species of rotifers, of which most are fresh-water inhabitants.
PHYLUM BRYOZOA
These colonial animals, known as “sea mats” or “moss animals,” form flexible tufts or thin incrustations over the surface of solid objects both in intertidal and deep waters. Below low tide, many species form rigid, erect, latticed or branched colonies. The individual minute animals have calcareous protective skeletons and possess a ring of ciliated tentacles for gathering microscopic food. There are over 3000 species, about 35 of which are nonmarine.
PHYLUM BRACHIOPODA
Brachiopoda are ancient sessile animals superficially resembling bivalve molluscs, but the hinged calcareous or horny shells are dorsoventrally situated instead of laterally, as in the molluscs, and the animals gather their food by means of delicate ciliated arms attached within the shell. They grow permanently attached to rocks and shells, usually in the littoral zone below low tide. A few live in burrows. All are marine and all are very abundant as fossils in the Paleozoic and Mesozoic rocks. About 120 living and 3500 fossil species are known.
PHYLUM PHORONIDEA
Phoronidea are wormlike animals, living in membranous tubes in the sand and collecting food by means of ciliated tentacles. There are about 12 marine species.
PHYLUM CHAETOGNATHA
Chaetognatha include numerous but small (maxima about 75 mm long) holoplanktonic wormlike animals known as “arrow worms” or “glass worms.” They are highly transparent and provided with eyespots, a caudal fin and one or two pairs of lateral fins, and with strong chitinous jaws and teeth for capture of prey. They occur from the surface to great depths and are distributed far to sea in all latitudes. All 30 known species are marine. Sagitta (fig. 228a) is the most abundant genus.
PHYLUM ANNELIDA
Annelida are true worms with elongated bodies composed of a series of similar segments.
Order Polychaeta. These are marine worms of great abundance provided with many setae and typically with a variety of well-defined head structures such as eyes, tentacles, chitinous jaws, ciliated cirri, and so forth, which are modified in keeping with their habits of life and mode of feeding. They have a wide distribution horizontally and bathymetrically.
Order Oligochaeta. These are earthworms, of which only a very few are marine, living near shore.
Class Echiuroidea. These are fleshy marine worms with only one or two pairs of setae. They are unsegmented or indistinctly segmented in the adult. They live in burrows in the mud and sand of the littoral zone. There are about 20 species.
PHYLUM ARTHROPODA
Arthropoda include animals with a segmented, chitinous exoskeleton and with jointed appendages, variously modified for locomotion, feeding, and other activities.
Class Crustacea. Entomostraca. This group, formerly considered a subclass, is of convenience in designating a large assemblage of small, primitive crustacea belonging to several subclasses and orders distinguished from the higher crustacea, or Malacostraca.
Suborder Cladocera. Only a few occur in the sea. Examples: Podon, Evadne, sometimes important in neritic plankton. Very numerous in fresh water.
Order Ostracoda. This order includes more than 2000 species, mostly marine, living in the plankton and on the bottom (fig. 227b).
Order Cirripedia. These are the barnacles which as adults have calcareous shells and live sessilely in all benthic habitats, especially coastal. Some grow attached to drifting objects or upon whales and other animals, or they may form special floats for suspension. There are about 500 species, all marine.
Order Copepoda. Though small in size (about 0.3 mm to 8 mm in length), the copepods bulk large in the animal substance of the sea, for they are by far the most abundant of all crustaceans and usually constitute about 70 per cent of the zooplankton. There are over 6000 species of copedods, found mostly in the sea, where some 750 species are planktonic and extremely numerous. Many others are benthic or parasitic. The three main suborders of free-living forms are Calanoida (fig. 227c), Cyclopoida (fig. 229d), and Harpacticoida (fig. 229a). The first two are mainly pelagic,
― 310 ―the last benthic. Like other Entomostraca and some Malacostraca, they gather food by means of fine bristles on certain appendages (p. 887).
subclass malacostraca. These are the large crustacea, mostly benthic, many with strong claws and biting mouth appendages.
Order Mysidacea. There are about 300 species, mostly marine, living on or near the bottom.
Order Cumacea. About 400 species of this order are known; nearly all are marine, benthic.
Order Euphausiacea. These are commonly known as “krill,” and in some regions are very abundant in the plankton and near or on the bottom. Some attain a length of about 50 mm, and may at times be the major constituent of the zooplankton. There are 85 known species, all marine. Examples: Euphausia, Meganyctiphanes (fig. 227a).
Order Amphipoda. There are about 3000 species, nearly all marine, in various habitats.
Order Isopoda. Over 3000 species are known; they are mostly marine, living on the bottom and on vegetation or burrowing in wood. Examples: Limnoria, Munnopsis (figs. 77 and 221).
Order Stomatopoda. This order contains about 200 species, all marine, benthic, most common in shallow water of lower latitudes.
Order Decapoda. Decapoda include crabs, lobsters, shrimps. They are widely distributed in both the pelagic and benthic regions. Most of the over 8000 species are marine.
Class Arachnoida. This class is well represented in the sea by a number of marine mites, over 400 species of sea spiders or pycnogonids, and 5 species of Limulus, the king crab. All are benthic.
Class Insecta. Only one insect is submarine during its whole life; a few others live on the foreshore or skip over the surface in search of food. Example: Halobates.
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA
The molluscs are noted particularly for their construction of an infinite variety of calcareous shells encasing the body and for the structural modifications that have taken place in the soft parts known as the foot and the mantle. These modifications are associated with the method of locomotion and capture of food.
Class Amphineura. The chitons are all flat, benthic animals creeping with the aid of a broad, flat foot. There are about 630 species, all marine.
Class Scaphopoda. Tusk shells live in the bottom mud from shallow water to depths of over 5000 m. All 200 known species are marine.
Class Gastropoda. In most types there is a spiral shell, and the foot is used in creeping. In this and the preceding classes a rasplike radula is a characteristic food-gathering organ. Some gastropods are holoplanktonic and may be without shells. These are the marine pteropods and heteropods (about 90 species of each) with the foot modified for swimming (fig. 228d,f). The latter are especially characteristic of the oceanic waters of the lower latitudes. There are about 49,000 species in the class, mostly marine.
Class Pelecypoda. The clams, oysters, and mussels have a hatchet-shaped foot which in many is used for digging. All are benthic, usually sessile or burrowing in mud, rock, or wood. The soft parts are enclosed within hinged shells and the food is conveyed to the mouth by means of ciliary action setting up water currents, sometimes through long siphons. There are about 11,000 species, of which about four fifths are marine.
Class Cephalopoda. In the squids, devilfish, and so forth, the foot is divided to form arms used in capture of prey. In keeping with their active, predacious habits, the eyes are usually well developed, but blind deep-sea forms occur. In Nautilus and related forms there is a well-developed shell. Cephalopods are either benthic or pelagic, some living at great depths. The giant squid, Architeuthis princeps, having a body girth of nearly 1 m and attaining a total length of about 16 m, is the largest of all invertebrates. There are about 400 species, all marine.
PHYLUM ECHINODERMATA
Echinodermata are animals with calcareous plates forming a more or less rigid skeleton, or with scattered plates and spicules embedded in the body wall. Many are provided with spines. All are marine, and all but a few sea cucumbers are benthic.
Class Holothuroidea. The sea cucumbers are mainly benthic. only members of the order Pelagiothurida being planktonic. There are over 650 species, some living in abyssal regions.
Class Asteroidea. The sea stars are among the most conspicuous of shore animals, but they live also at very great depths. About 1100 species are known.
― 312 ―Class Ophuroidea. There are more than 1600 species of brittle stars, with a wide horizontal and bathymetric distribution.
Class Echinoidea. There are about 600 species of sea urchins and sand dollars, a few of which live in deep water.
Class Crinoidea. About 800 species of sea lilies and sea feathers are known, with the center of distribution in the East Indian waters, but they also occur in many other waters. The former live mainly in the deep sea and are anchored by long stalks. The latter occur mainly at shallower depths and are without stalks. The class is a vanishing remnant of a formerly abundant group that has left more than 2000 fossil species.
PHYLUM CHORDATA
Chordata are animals which in some stage of their life have gill slits and a skeletal axis known as a notochord.
Subphylum Tunicata. These are primitive chordates; of about 700 species, all are marine.
Class Larvacea (Appendicularia). These are small planktonic forms, sometimes abundant. Examples: Oikopleura (fig. 228e), Fritillaria.
Class Ascidiacea. These are sessile ascidians such as Ciona and Culeolus.
Class Thaliacea. This class is made up of pelagic tunicates that float singly or in chains; they may be very abundant at the surface in the warmer waters. Examples: Salpa, Doliolum.
Other protochordates are the wormlike Enteropneusta and the fishlike Cephalochorda, both of which are found burrowing in mud and sand.
VERTEBRATES
Subphylum Vertebrata. This group includes animals with vertebrae. All but the classes Aves and Mammalia are cold-blooded.
Class Cyclostomata. The hagfishes and lampreys are fishlike forms but without paired fins. They have a circular sucking mouth without jaws. The former are all marine, while the latter live both in the sea and in fresh water.
Class Elasmobranchii. These primitive fishes—the sharks, rays, and chimaeras with a cartilaginous endoskeleton—have paired fins and a lower jaw. In this group are many large forms such as the giant manta and the whale shark, the largest of all fishes, which becomes about 16 m long. Nearly all are marine.
Class Pisces. This class includes the true fishes, with a bony endoskeleton, paired fins, and an operculum covering the gills. They are characteristically streamlined for great swimming
Class Reptilia. This class is represented in the sea by snakes and turtles. They breathe air and are therefore inhabitants of surface waters. The turtles frequent the shore to deposit their eggs on sandy beaches; the snakes bring forth living young and are therefore less dependent upon the shore. The sea snakes are found in the Indo-West Pacific and in tropical waters of America. They grow to a length of from 1 to 2 m or more and some are very poisonous. The sea turtles occur in tropical and subtropical seas. They have paddlelike limbs for swimming, and some grow to great size. The leathery turtle, for example, which is the largest of the class, may attain a weight of 1000 pounds.
Class Aves. A great number of birds are dependent upon the sea for food. Some of these frequent the land only for nesting and rearing of young. Typical examples are the albatrosses, petrels, cormorants, and auks.
Class Mammalia. These are warm-blooded, air-breathing animals with hair and mammary glands.
Order Carnivora. The marine members of this order are the sea otters and, to a lesser degree, the polar bears. The sea otters occur only in small numbers and only along the west coast of North America, where they were formerly hunted commercially to the very verge of extinction. Recently, under rigid protection, they have recuperated to an encouraging degree. The polar bears are confined to the Arctic region, usually on or near floating ice
Order Pinnipedia. Pinnipedia include seals and walruses, nearly all marine. The limbs are finlike, in adaptation to the aquatic existence. There are three families: (1) Otariidae include the eared seals, sea lions, and fur seals. Small external ears are present and the hind limbs can be rotated forward. (2) Phocidae are the hair seals without external ears and with hind limbs incapable of rotation forward. (3) Odobenidae include the walruses, with greatly elongated canine teeth in the upper jaw. They are confined to the Arctic.
Order Sirenia. Sirenia are heavy-bodied mammals with a flat tail and with forelimbs modified as paddles. Hind limbs are wanting. They live near shores in warm waters,
― 314 ―where they browse upon vegetation. They are not numerous. Examples: sea cows, manatees, and dugongs.Order Cetacea. This order includes whales and dolphins, highly modified for aquatic life by a streamlined body and finlike forelimbs and tail. The hind limbs are wanting.
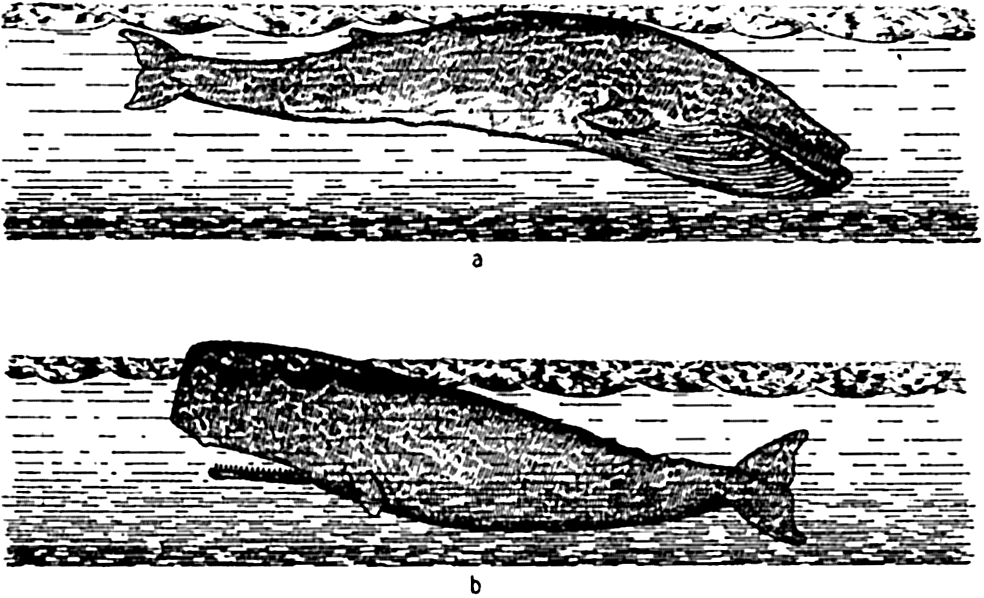
Suborder Mysticeti. These are the baleen, or whalebone, whales, with a series of long plates of baleen suspended in the mouth (fig. 76a). The frayed ends of these are used in screening out plankton food. Examples: fin whale, humpbacked whale, and blue whale. The last named is the largest of all animals, growing to a maximum length of about 34 m and weighing 294,000 pounds.
a, the blue whale—a whalebone whale; b, the sperm whale—a toothed whale.
Suborder Odontoceti. Odontoceti are the toothed whales. This group includes (1) sperm whales with teeth only in the lower jaw (fig. 76b) and (2) the numerous dolphins and porpoises with teeth in both jaws.
Reproduction and Life Cycles in Marine Animals
In any comprehensive study of oceanography wherein biological activities are implicated or in the study of any population or individual species in relation to environmental factors, it is necessary to take into consideration the nature of the life cycles of the organisms involved. Only thus can the biological activities and the methods whereby the race is maintained through countless numbers of generations be fully understood. The utility of life-cycle studies in such practical fields as economic entomology, parasitology, and fisheries has been abundantly demonstrated. Through a knowledge of the methods of reproduction and through recognition of the various developmental stages of marine animals the investigator has at hand valuable means of aiding the interpretation
It should be pointed out here that, in dealing with the propagation of any individual species in relation to its distribution, we must distinguish broadly between (1) reproductive distribution and (2) sterile distribution. Reproductive distribution is associated with areas where environmental conditions are favorable to maturation, spawning, and larval development. Such areas may be called areas of reproduction, or nursery areas. Sterile distribution is associated with areas in which the submature or adult individuals may live and some spawning may take place, but in which the eggs fail to hatch or the larvae do not survive, so that the area must be restocked periodically by invasion of postlarval stages produced elsewhere.
In a study of the life cycles of marine animals, one is impressed particularly with three facts: (1) the preponderance of animals which, though sessile, creeping, or burrowing in the adult stage, possess a free-swimming period during the early stages of life; (2) the enormous numbers of young that are produced by both pelagic and benthic animals; and (3) the fundamental similarity of the larvae of different invertebrate groups. We shall be concerned only with the first two.
In a superficial survey of populations, it is mainly the larger, more conspicuous adult animals that are seen, yet, from the standpoint of numbers, vastly more starfish, barnacles, clams, crabs, fish, and so on, are represented in the microscopic, feebly swimming larval stages than in the adult stages. Most of these larvae do not survive to assume the adult habit, but, instead, serve as nourishment for other organisms, swimming or sessile, or are in some manner destroyed through action of the physical or chemical environment.
Types of Reproduction. In reproduction, animals are either oviparous or viviparous. The oviparous forms deposit eggs that develop outside the mother's body, while in the viviparous forms the young are nourished by the mother and are born alive in a postembryonic state. An intermediate condition exists in the ovoviviparous forms, where the eggs are incubated and hatched within the body, as in certain sharks, perch, and blennies. The term larviparous is sometimes used to indicate that larval stages are born. An embryo derives its nourishment from the yolk of the egg or directly from the mother, whereas typically a larva is morphologically adapted with mouth and digestive tract for the purpose of seeking its own nourishment. Later it will be seen how important this fact is in the life of many marine animals.
By far the greater number of animals of the sea are oviparous, and it is among these that the extraordinarily large numbers of eggs are
| American oyster | 115,000,000 | Pacific halibut | 3,500,000 |
| Sea hare (Tethys) | 478,000,000 | Cod | 4,400,000 |
| Teredo navalis, more than | 2,000,000 | Sunfish (Mola) | 300,000,000 |
Parental care of eggs and larvae.
It has long been recognized, however, that the exceedingly great number of eggs produced by some species is not directly correlated with the number of adults that are found. The large numbers of eggs and larvae produced are, instead, a measure of the tremendous toll paid by these species in order to assure survival of enough individuals to carry on the race.
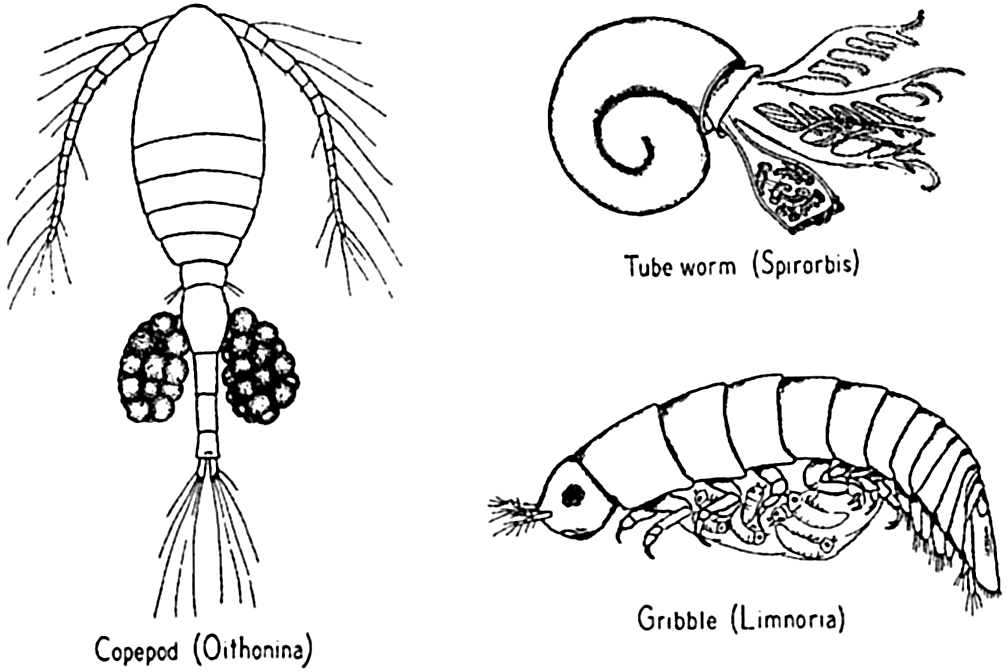
In the marine population as a whole, very little parental protection is given to the offspring in the larval stages, and frequently even the eggs are given no care, yet hundreds of examples can be cited wherein varying degrees of protection are afforded the embryonic stages and sometimes the larvae as well. Many of the larger crustacea retain the developing eggs attached by secretions to hairlike structures on the abdominal appendages. Some annelids produce viscid secretions for attaching the eggs to setae or to the body wall, while others retain the young up to a well-developed larval stage in special brood pouches, as in Spirorbis (fig. 77). Many other invertebrates provide brood pouches—for example,
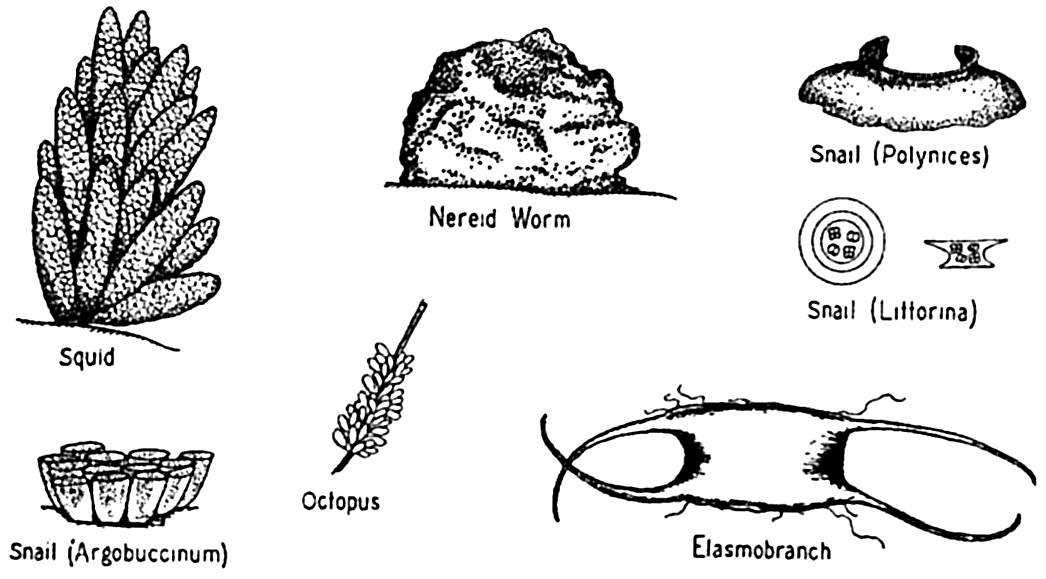
Some types of egg cases for protection of eggs and larvae.
It is clear that in these instances of parental protection the need for large numbers of eggs is somewhat diminished. Nevertheless, when a relatively long, helpless, pelagic stage follows the protected period of incubation, many larvae must still be produced. Thus, for instance, the blue crab, which, though protecting the eggs till the young are hatched, has pelagic larvae and is said to carry over two million eggs (Truitt, 1939). In contrast, Limnoria produces a maximum of only about-twenty-five eggs, but retains these within a pouch until the young are able to burrow into the wood where they were born. Thus they escape the hazardous pelagic life of larvae. In this animal the hazards of a swimming existence are met not by the very young but by submature specimens which by short migrations attempt to establish themselves in less crowded situations prior to breeding (Johnson, 1935). The fact that some animals produce more eggs than others and at the same time offer more parental care must indicate that factors operate to destroy more developing young in one than in the other.
Finally should be mentioned the common method of depositing eggs in masses or protective capsules of various types (fig. 78), thus diminishing loss from excessive dispersal and other hazards of a floating existence during the period of incubation. The capsules are also sometimes
Types of Development. There are two main types of development: (1) direct and (2) indirect. The direct development in oviparous species is associated with eggs of considerable yolk content, such as are found in the fishes, cephalopods, some nemerteans, crustaceans, and others. The newly hatched young are similar to the parent except for size.
Direct development is common among the deep-sea benthic animals, and this habit appears to be an advantageous adaptation. The slowly moving currents of great depths are of less importance in the dispersal of larvae than are the stronger currents of shallow water. The micro-planktonic life so characteristic of surface layers and from which the pelagic larvae of littoral animals directly derive their food has no counter-part in the deep, and hence it is imperative that the young produced be able to feed directly upon the bottom detritus. The possibility of deep-sea larvae swimming from great depths to the surface, where food is plentiful, and later returning to the bottom appears to be impracticable in nature. The young of some mid-depth pelagic forms—for example, Cyclothone among the fishes and Acanthephyra among the prawns—do however live nearer the surface, where food is more plentiful, than where the adults are commonly to be found (Hjort, 1912).
Benthic animals of Arctic and Antarctic regions also commonly possess no pelagic larval stages. Hjort (1912) and Murray (1913) consider this a probable explanation of the great local concentrations of certain boreal and arctic benthic animals, because the direct development results in the young remaining in the area in which they are born. Brief pelagic larval stages following protection during incubation and absence of dispersing currents lead also to local adult concentrations.
The indirect development is associated with a type of egg with little yolk (that is, alecithal), and hence a self-sustaining larva must develop quickly or the organism dies. This type of development is characteristic of marine invertebrates, which usually cast their eggs free in the water or carry them through the incubative period in special brood pouches. Larval stages appear before the full character of the species to which they belong becomes established. Many of these—for example, the pluteus larvae of the Echinoidea and the Ophuroidea—when first discovered were described as distinct kinds of animal, only to be found later to be the young of already well-known species. The locomotor organs of most of the larvae are cilia (see below for exceptions) which by their rhythmic beating propel the animal slowly through the water at a rate just sufficient to keep them in suspension. The great similarity of structure exhibited by the larvae of some groups suggests a common origin for the groups which as adults are structurally very dissimilar.
Typical Life Cycles. The life cycles of many species have not been investigated, but the principal features in the life history of the major groups have been established. We shall here review only the groups of most immediate interest in general oceanographic studies.
In the protozoa, reproduction is mainly by binary fission, whereby the animals divide to form two separate animals, these in turn dividing after growth. Under favorable conditions, this method makes possible a production of great masses of individuals, as is often witnessed in such forms as Noctiluca. Gametes are also formed in this animal as a result of multiple fission. These unite in pairs, but their further development is unknown. In foraminifera, and possibly also in radiolaria, there is a cyclical alternation of generations in which sexual and asexual phases alternate and give rise to morphologically different individuals (Myers, 1936).
In the tintinnids, in which transverse binary fission occurs, the anterior daughter escapes from the lorica, while the posterior daughter retains the old lorica (Kofoid, 1930).
The sponges reproduce asexually by budding or fragmentation, and sexually by union of gametes, the latter resulting in a free-swimming, flagellated larva, the amphiblastula, which, after a period of swimming, settles to the bottom and grows to form the adult sponge. Asexually produced units, known as gemmules, possessing a heavy protective covering are produced by some sponges as a means of survival during adverse periods. Reproduction by formation of gemmules occurs principally among the fresh-water sponges, but some marine forms also produce gemmules.
In the coelenterates, both sexual and asexual reproduction are important features in the life cycle. The union of germ cells results in a free-swimming, ciliated, planula larva about 1 mm long (fig. 80c). The planulae, though lacking the mouth and enteron of typical larvae, may live for a sufficiently long period on yolk food to bring about dispersal of sessile coelenterates such as the corals and anemones. Vaughan (1919) found the pelagic period of corals to be from one day to two or three weeks. Upon settling to a hard bottom the planulae of corals and other Anthozoa develop a mouth and tentacles for feeding, and later the reproductive organs are formed. In some there is also active asexual reproduction by fission and budding. Large coral colonies are thus initiated from a single individual. It is the skeletons of these asexually produced individuals which form the large coral heads, some of which are 3 m or more in diameter and contain many thousands of individual polyps. The length of time required for formation of such colonies has been investigated by Vaughan (1919), who found that a coral colony (Porites asteroides) 50 mm in diameter may be formed in four years.
The remarkable life histories of many jellyfish of the class Hydrozoa offer the examples of alternation of generations that are used in all zoological texts. The jellyfish, or medusa, stage (fig. 79) of such forms as Obelia is either male or female, and the eggs are cast free in the water, where they are fertilized and develop into planula larvae. The planula soon settles on the bottom to form the sessile polyp, or hydroid, stage. From special structures on the polyp, asexually produced buds become separated as swimming medusae, thus completing the cycle. The alternation of sessile and pelagic generations is a factor of great significance in the distribution not only of the hydrozoa such as Obelia, but also of other forms—for instance, the large scyphozoan Aurelia, which, though varying in details of life history, possesses stages similar to those in Obelia. The sessile generation is the chief link instrumental in restricting all stages of such animals to the neritic waters, generally to the proximity of shores and shoals with a suitable substratum of rocks, shells, or larger plants for attachment of the planula larvae. Bigelow (1938) found that in the open sea off Bermuda only about 3 per cent of the medusae caught at a distance of 10 miles from shore were of the type with a fixed stage in their life history. The degree of dispersal is, of course, dependent upon the speed and direction of the water currents prevailing. Some swimming jellyfish—for example, Aglantha digitalis and other members of the order Trachylina—are not dependent upon a sessile stage because daughter medusae develop directly from the pelagic stages.
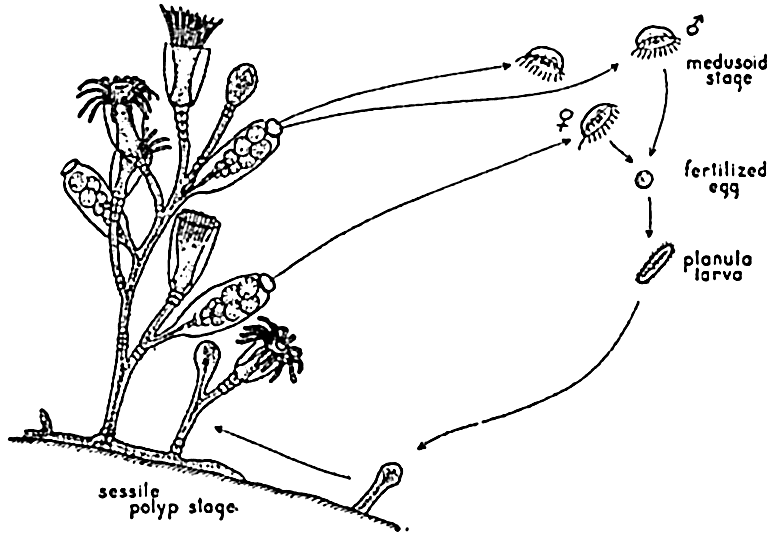
The life cycle of a typical hydrozoan jellyfish, Obelia.
Open-sea colonial coelenterates—for example, Velella or Physalia—are representatives of the “blue-sea fauna.” Their life cycle is adapted to offshore life by elimination of the sessile stage. The planula larva gives rise to a medusiform stage from which the complicated colony arises.
The Ctenophores are all hermaphroditic, and the eggs are usually shed into the water, where, upon fertilization, they grow by direct development into free-swimming larvae. Gastrodes, a parasite in Salpa, produces a typical planula larva.
The great importance of annelids, especially in the littoral benthic fauna, warrants their inclusion in this brief study of life histories. At certain seasons the voracious swimming larvae of annelids are a major
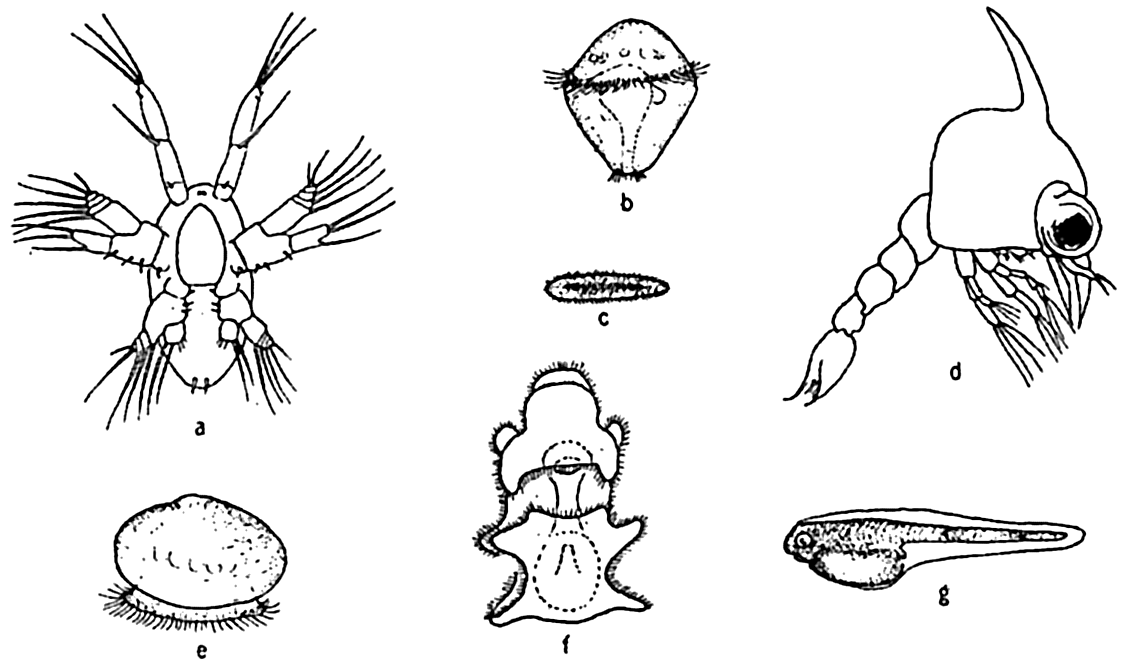
Some characteristic marine larvae. a, nauplius larva of the copepod Labidocera; b, trochophore larva of the annelid Nereis agassizi; c, planula larva of coelenterates; d, zoea larva of the crab Pachygrapsus; e, veliger larva of the clam; f, bipinnaria larva of starfish; g, the cod larva with yolk sac.
The larvae of many benthic annelids enter the plankton only after they have completed their early stages under some means of special protection. For example, in the little tube worm, Spirorbis, and related forms, they develop in a special brood pouch beneath the operculum, while in some Polynoe, or scale worms, they are sheltered by the dorsal, flaplike elytra, and in yet other instances the eggs are deposited in attached or demersal gelatinoid masses (fig. 78), where the developing embryos and larvae enjoy some degree of protection. In Spirorbis the trochophore stage is passed in the brood pouch and the older larvae may assume the sessile habit after only twenty-four to thirty-six hours in the plankton. If a suitable substratum is not available, the pelagic stage is somewhat prolonged. Nereis agassizi spawns the eggs free
The chaetognaths, or arrow worms, are hermaphroditic but not self-fertilizing. The eggs, which are fertilized internally, are shed into the water, where they develop directly into free-swimming larvae not unlike the adults.
Most crustaceans, in which we are particularly interested because of their prominence in some phases of oceanographic studies, pass through several distinct pelagic larval stages. The common initial crustacean larva is the nauplius (fig. 80a), bearing three pairs of appendages used for both swimming and feeding.
In copepods the sexes are separate, in some species the ratio of adult males to females being strikingly unequal at all times, while in other species the inequalities are seasonal, the males being more abundant at the onset of breeding but later diminishing in numbers more rapidly than the females after the breeding season (Damas, 1905, Farran, 1927, Campbell, 1934). The most important of the planktonic copepods spawn the fertilized eggs free in the water, yet many littoral species and some important pelagic species—for instance, Oithona, Paraeuchaeta, and others—carry the eggs in brood sacs through the period of incubation (fig. 77). In both cases the eggs hatch to typical self-sustaining nauplii. Paraeuchaeta is somewhat of an exception, for it develops from a heavily yolked egg and does not feed in the naupliar stage (Nicholls, 1934). In copepods there are normally six successive naupliar stages separated by definite moulting of the chitinous skin. The hard exoskeleton of crustaceans does not grow, and must therefore be shed or moulted periodically as the animal becomes too large for the encasement. In many crustaceans the number of moults may be variable, but in copepods there are a fixed number of stages, each separated by a moult. At the termination of the sixth naupliar stage a complete metamorphosis occurs from which emerges Stage I of six successive copepodid (copepodite) stages. Copepodid Stage VI is the adult, and, during spring reproduction in waters of the latitude of the British Isles, maturity may be reached in a period of about twenty-eight days in Calanus finmarchicus, but it is much delayed in the autumn-winter generation or in populations of more northern waters.
In Calanus finmarchicus, by far the most thoroughly investigated of all pelagic copepods, it has long been known (Gran, 1902, and others) that the animals spend the winter months in the deeper water layers. The breeding of this species occurs in spring and summer in boreal waters, and there are two or more successive generations, each of which, apparently, may bear more than one brood. The generation arising from the first spring spawning appears to mature quickly, spawn, and die. The last generation produced in autumn is a relatively long-lived
The life cycle of Calanus finmarchicus appears to be quite characteristic of other members of that important genus and perhaps of other related genera as well, but very few pelagic copepods have been adequately investigated, and considerable variation can be expected. We shall not enter into the remarkable life histories of the parasitic copepods, but an example of a typically free-living littoral form—that is, Tisbe furcata—is instructive for comparison with Calanus. Tisbe furcata carries the eggs through the incubative period in brood sacs. There are six naupliar and six copepodid stages, as in Calanus but the time required for development from egg to mating maturity may be as little as ten days, and filled egg sacs are carried by females of the new generation in fourteen days after hatching. During maximum production, one female may produce at least seven or eight broods at about five- to eight-day intervals.
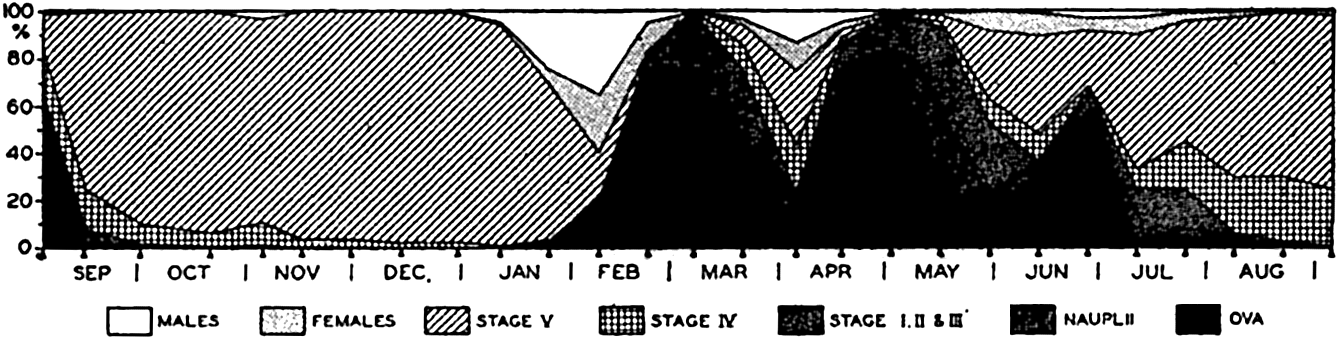
Successive generations of Calanus finmarchicus (from Nicholls).
In the euphasiids, another group of outstanding importance in the economy of the sea, the method of reproduction is not unlike that occurring in many copepods, in that usually the eggs are shed in the water, but the succession of generations is not rapid and the life span is of greater length. For Euphausia superba, in Antarctic waters, the time required to reach sexual maturity is estimated by Ruud (1932) to be two years. Some investigations indicate that normally the animals live in the immediate vicinity of the bottom and that during spawning they congregate in swarms and ascend to deposit the eggs in surface-water layers. Here, while slowly sinking, the eggs hatch to typical naupliar larvae, which are followed by successive stages of distinctive larvae, the older of which may return for a time to the surface layers. In
Among most other crustaceans the eggs are carried through incubation attached to appendages or in brood pouches of various types. In heavily yolked eggs, as in the common crab and related forms, the nauplius stage is passed within the egg, and the developmental stage emerging from the egg is known as a zoea larva (fig. 80d), of which there may be several separate stages. The weakly swimming zoea may drift in the plankton for several weeks before changing to the megalopa stage and settling on the bottom. The lobster produces a special type of pelagic larva. the phyllosoma, which, with its leaflike body, is especially adapted to float in the plankton (fig. 229g). In barnacles, the larvae escaping from the mantle cavity within the shell of the sessile adult are typical nauplii which, after living a pelagic existence for a few weeks, are transformed into what are called cypris larvae (fig. 2241). The cypris larvae soon settle to the bottom and, upon attachment to a solid surface, metamorphose to assume the adult state.
In most bivalve (pelecypod) molluscs the sexes are separate, although some are hermaphroditic, and others—for example, certain species of oysters—are unisexual but change their sex alternately from one to the other. This phenomenon is also observed in other marine animals (Coe, 1940). Fertilization of the eggs frequently takes place after the eggs have been shed into the water, but commonly the eggs are retained within the brood pouch formed by the gills, in which case the spermatozoa are taken in through the inhalant siphon with the stream of water that is kept flowing over the gills. A modified trochophore larva is first formed, and from this a later larva, the veliger, results (fig. 80e). After a period of swimming the veliger settles to the bottom.
Gastropods are often hermaphroditic. Fertilization among them is commonly internal, and their eggs are frequently deposited in gelatinous or membranous cases attached to rocks or sea weed. Tiny floating cases containing several eggs are sometimes formed, as in Littorina (fig. 78). The trochophore and part of the veliger stage are passed within the egg case.
Among the echinoderms the sexes are separate and the eggs are usually spawned into the water, where fertilization occurs. Some (Asterina) lay demersal eggs which, because of their viscid nature, adhere to rocks and other objects. In other echinoderms, especially deep-sea and polar species, the eggs are fertilized and retained in brood pouches, where they undergo early development. Development is indirect in all cases, but the forms with most heavily yolked eggs do not have pelagic
The metamorphosis resulting in the adult state is as complete as that experienced by the butterfly, and it is not surprising that, before the parentage of the pelagic larvae was known, they were considered as distinct animals unrelated to the adult (figs. 80f and 224f and j). The characteristic larvae are bipinnaria (sea stars), echinopluteus (sea urchins), ophiopluteus (brittle stars), auricularia (sea cucumbers). The echinoderm larvae are of only moderate interest in the economy of the sea, but great biological interest is attached to the probable significance of some in showing a relationship to the most primitive chordates.
Many fishes—for example the cod, mackerel, halibut, and sardine—shed their eggs into the water, where fertilization takes place and the developing larvae are nourished by the yolk of the floating eggs (fig. 80g). The herring deposits viscid eggs which, upon sinking to the bottom in shallow water, become attached to solid objects. The gobies, blennies, sculpins, and others attach their eggs to solid objects or lay them on the bottom, where the male may stand guard over them until hatched. The grunion buries its eggs in the sand of wave-washed beaches during periods of high spring tide. Here the eggs remain for a period of about two weeks, when the next series of high tides washes them out and stimulates their hatching (Thompson, 1919, Clark, 1925). In sharks and rays, fertilization is internal, and either the young are born alive or the nonbuoyant eggs are deposited in leathery cases known as “mermaids, purses” (fig. 78, p. 317).
The eggs of fishes fall roughly into two groups, depending upon buoyancy: (1) pelagic and (2) demersal. The demersal eggs sink to the bottom or are deposited there; pelagic eggs float freely in the water and hence greater numbers are produced to overcome the losses inherent with this group. Many fisheries investigations are concerned with the occurrence and dispersal of pelagic eggs and the resulting larvae, for from such studies much information is gleaned regarding the spawning habits and areas of many commercially important fishes (p. 861). In general, the development of fishes can be considered as being direct, there being no general metamorphosis of form to the adult morphology. There is frequently, nonetheless, a marked degree of dissimilarity between larvae and adult, and in some there is a distinct metamorphosis. The Leptocephalus larva of the eel, for instance, was once considered a separate species. Many fishes have definite spawning grounds far removed from their feeding habitat, and the remarkable migrations of such fishes as the eel and the salmon are directly associated with reproductive instincts (pp. 811 and 861).
The reproductive habits of certain deep-sea fishes are of special interest as an indication of adaptation to the environment. In the lightless,
The mammals of the sea bring forth living young, which are nursed for a period by the mother. Like those of some fishes, the great migratory movements of whales and seals are associated with wanderings to and from favorable breeding grounds. Growth in whales is extremely rapid; sexual maturity may be reached in two years, and one calf may be produced every other year.
The spawning of many marine animals, especially in boreal waters, is of a spontaneous nature, and vast numbers of individuals spawn within a period of a few days, with the result that in such cases the main spawning period is easily ascertained, since great swarms of eggs or larvae appear suddenly in the plankton and are gradually dispersed by water movements. This feature is especially well illustrated by the oyster, certain sea cucumbers (Cucumaria), nereid worms, and barnacles.
The degree of success of (1) spawning or (2) survival of larvae of successive spawning seasons gives rise to an inequality in numerical strength of year classes of adult or juvenile forms constituting any given population. This inequality is best demonstrated by studies of commercial fishes, investigations of which have been most ardently pursued. However, the same inequality must also occur in the populations of any animals with a normal life span sufficiently long for individuals to live through several reproductive seasons as juveniles and adults.
For purposes of illustration we may consider a species with a life span of several years in which the age of individuals can be accurately determined and in which adequately large and inclusive samples are obtainable for comparison. Now, assume a highly successful spawning and larval survival in a moderate population of this species in the breeding season of 1930, a very poor spawning season in 1931, an average degree of spawning and survival of larvae in 1932, and then another highly successful year in 1933. The 1930 year class will, upon investigation of the whole population in 1931, show up as a disproportionately great number of small, one-year-old individuals in relation to the other age groups in the population. In the next year (1932) the two-year-old individuals of the 1930 spawning are still conspicuous in the population, but the smaller number of one-year-old individuals is evidence of a poor spawning or survival for the 1931 reproductive season. Thus, in 1933 and subsequent years the downward trend of numerical strength of the 1930 and 1931 classes can be traced and compared with other year classes—for example, that of the average year 1932 and of the successful year 1933
From such comparative studies of year classes and with a knowledge of the spawning habits and age groups, means are provided for analysis of probable environmental factors that determine the degree of success of spawning or survival of larvae, because the relative number of individuals entering into any year class must depend mainly on these critical periods. In subsequent years within the normal life span of the species, the reduction of numbers in year classes is not so likely to be of catastrophic nature. It has been pointed out by Hjort et al (1933) that for a given region the average rate of growth of individuals within the different year classes of Norwegian herring is the same for each year class regardless of the relative numerical strength of the classes. This seems to indicate that, in the sea, nature each year provides a sufficiency of food for the survival and growth of the older stages of this fish as represented in the composite commercial catch. The numbers of individuals belonging to the separate year classes may be widely different (as much as 1 to 30), and this difference must then result from some factor or multiplicity of factors operating to destroy the animals during the very early stages of their existence.
Schematic illustration of changes in year class composition of a population.
Studies of commercially important fish, shellfish, and whales are deeply concerned with analysis of the year classes. For example, in nature there is an equilibrium between the rate at which fish enter the accumulated stock or supply and the rate at which they are withdrawn through natural mortality. Additional removal through fishing exploitation disturbs this equilibrium and may constitute so serious a drain upon the stock that the drain becomes greater than the rate of replenishment and the stock subsequently becomes so depleted that it is no longer
Year-class analyses of the fish population are also utilized as a basis in arriving at forecasts of the most probable abundance of fish in the next year's catch. Illustrative of this are the investigations of the U. S. Bureau of Fisheries into the fluctuations so characteristic of commercial catches of mackerel. Sette (1931et seq) studied the relative abundance of these fish caught with reference to each year class of the population. The numerical strength of the younger year classes entering into the catch provided a basis for calculating the probable yields that these classes would give in the following year under similar conditions of fishing. Such calculations can be significant only when the downward trend in numbers of the dominant year classes is rather regular. In dealing with migratory fishes, the occurrence of sporadic invasions of populations produced elsewhere or with a different range and whose year-class composition is not known must give rise to unexpected changes in the ratio of the year classes occurring in any one range or locality under investigation. The continued success of such commercial fisheries as the mackerel is determined mainly by the numerical strength of the dominant year classes of the population native to the fishing area. In the above investigation it was found that the big year class of 1923 constituted the main bulk of a declining fisheries yield for a period of years until the industry again experienced a sharp upward incline as the contingents of the 1928 successful spawning entered the catch.
Bibliography
Arber, A.1920. Water plants. London. Cambridge Univ. Press.
Bigelow, H. B.1938. “Plankton of the Bermuda Oceanographic Expedition. VIII. Medusae taken during the years 1929 and 1930” . Zoologica, v. 23, p. 99–189, 1938.
Campbell, M. H.1934. “The life history and post embryonic development of the copepods, Calanus tonsus Brady, and Euchaeta japonica Marukawa. Canada” , Biol. Board, Jour., v. 1, p. 1–65, 1934.
Clark, Frances N.1925. “The life history of Leuresthes tenuis, an atherine fish with tide-controlled spawning habits” . Calif. Fish and Game Comm., Fish Bull.no. 10, p. 1–51, 1925.
Coe, W. R.1926. “The pelagic nemerteans” . Harvard Coll., Mus. Comp. Zool., Mem., v. 49, 244 pp., 1926.
Coe, W. R.1940. “Divergent pathways in sexual development” . Science, v. 91, p. 175–82, 1940.
Damas, D.1905. Notes biologiques sur les copepodes de la mer Norvégienne. Conseil Perm. Internat, p. l'Explor. de la Mer, Pub. de Circonstance, no. 22, 23 pp., 1905.
Ellis, B. F. and A. R. Messina. 1940. “A catalogue of foraminifera. New York” . Amer. Mus. Nat. Hist.30,000 pp.1940.
Farran, G. P.1927. “The reproduction of Calanus finmarchicus off the south coast of Ireland. Conseil Perm. Internat. p. l'Explor. de la Mer” , Jour. du Conseil, v. 2, p. 132–43, 1927.
Fritsch, F. E.1935. The structure and reproduction of the algae. Vol. 1, Introduction, Chlorophyceae, Xanthophyceae, Crysophyceae, Bacillariophyceae, Cryptophyceae, Dinophyceae, Chloromonadineae, Euglenineae, colorless Flagellata. New York, Macmillan. 791 pp., 1935.
Gail, F. W.1922. “Photosynthesis in some of the red and brown algae as related to light. Univ. Washington” , Puget Sound Biol. Sta., Pub., v. 3, p. 177–193, 1922. Seattle.
Gran, H. H.1902. Plankton des Norwegischen Nordmeeres von biologischen und hydrografischen Gesichtspunkten behandelt. Norwegian Fishery and Marine Investigations, Rept., v. 2, No. 5, p. 1–222, 1902. Bergen.
Gran, H. H.1912. Pelagic plant life. p. 307–86 in: Murray and Hjort, Depths of the ocean. London, Macmillan. 821 pp., 1912.
Hartge, L. A.1928. “Nereocystis. Univ. Washington” , Puget Sound Biol. Sta., Pub., v. 6, p. 207–37, 1928.
Hesse, Richard, W. C. Allee, and K. P. Schmidt. 1937. Ecological animal geography. An authorized, rewritten edition based on “Tiergeographie auf oekologischer Grundlage” by Richard Hesse. New York. John Wiley & Sons. 597 pp., 1937.
Hjort, J.1912. In: Murray and Hjort, Depths of the ocean. London, Macmillan. 821 pp., 1912.
Hjort, Johan, Gunnar Jahn, and Per Ottestad. 1933. The optimum catch. Hvalrådets Skrifter, No. 7, p. 92–127, 1933. Oslo.
Hustedt, F.1930 et seq. Die Kieselalgen. In: Rabenhorst's Kryptogamen-Flora, v. 7, 1 Teil, 2 Teil, 576 pp., 1930–1933. Leipzig. Akad. verlagsges.
Hyman, Libbie H.1940. The invertebrates: Protozoa through Ctenophora. New York, McGraw-Hill. 726 pp., 1940.
Johnson, Martin W.1935. “Seasonal migrations of the wood-borer Limnoria lignorum (Rathke) at Friday Harbor” , Washington. Biol. Bull., v. 69, p. 427–438, 1935.
Kofoid, C. A.1930. Factors in the evolution of the pelagic Ciliata, the Tintinnoinea. p. 1–39 in: Contributions to Marine Biology, Stanford Univ. Press, 277 pp., 1930.
Kofoid, C. A., and A. S. Campbell. 1929. “A conspectus of the marine and fresh-water Ciliata belonging to the suborder Tintinnoinea, with descriptions of new species principally from the Agassiz Expedition to the eastern tropical Pacific 1904–1905” . Calif. Univ., Pub. Zool., v. 34, 404 pp., 1929.
Kofoid, C. A., and T. Skogsberg. 1928. “The Dinoflagellata: The Dinophysoidae. Report, Albatross Exped. 1904–1905” . Harvard Coll., Mus. Comp. Zool. Mem., v. 51, 766 pp., 1928.
Kofoid, C. A., and Olive Swezy. 1921. “The free-living unarmored Dinoflagellata” . Calif. Univ., Mem., v. 5, 538 pp., 1921.
Lebour, M.1926. “A general survey of larval euphausiids, with a scheme for their identification” . Marine Biol. Assn. U.K., Jour., v. 14, no. 2, p. 519–27, 1926. Plymouth.
Murray, Sir John. 1913. The ocean: A general account of the science of the sea. London, Williams and Norgate, 256 pp., 1913.
Myers, E.1936. “The life cycle of Spirella vivipara Ehrenberg, with notes on morphogenesis, systematics and distribution of the foraminifera” . Roy. Microsc. Soc., Jour., v. 56, p. 120–46, 1936.
Nicholls, A. G.1933. “On the biology of Calanus finmarchicus. I. Reproduction and seasonal distribution in the Clyde Sea area during 1932” . Marine Biol. Assn. U. K., Jour., v. 19, no. 1, p. 83–101, 1933. Plymouth.
Nicholls, A. G.1934. “The developmental stages of Euchaeta norvegica Boeck” . Roy. Soc. Edin., Proc., v. 54, pt. 1, no. 4, p. 31–50, 1934.
Petersen, C. G. Joh. 1918. “The sea bottom and its production of fish food” . Danish Biol. Sta., Rept., v. 25, 62 pp., 1918. Copenhagen.
Pratt, H. S.1935. A manual of the common invertebrate animals exclusive of insects. Revised. Phila., Blakiston, 854 pp., 1935.
Ruud, J. T.1932. On the biology of southern Euphausiidae. Hvalrådets Skrifter, no. 2, 105 pp., 1932. Oslo.
Setchell, W. A.1912. Kelps of the United States and Alaska. U. S. Senate Document 190, Fertilizer resources of the United States, App. K, p. 130–178, 1912.
Sette, O. E.1931. Outlook of mackerel fishery in 1931. U. S. Bureau of Fisheries, Fishery Circularno. 4, 20 pp., 1931, et seq.
Thompson, W. F.1919. “Spawning of the grunion (Leuresthes tenuis)” . Calif. Fish and Game Comm., Fish Bull., no. 3, p. 1–29, 1919.
Thompson, W. F.1937. “The theory of the effect of fishing on the stock of halibut” . Internat. Fisheries Comm., Report no. 12, 22 pp., 1937.
Tilden, J. E.1935. The algae and their life relations, Fundamentals of phycology. Minneapolis, Minn., Univ. Press, 550 pp., 1935.
Truitt, R. V.1939. Our water resources and their conservation. Chesapeake Biol. Laboratory, Contribution no. 27, 103 pp., 1939.
Vaughan, T. W.1919. Corals and the formation of coral reefs. Smithsonian Inst., Report for 1917, p. 189–276, 1919.
Wilson, D. P.1935. Life of the shore and shallow sea. London. Ivor Nicholson and Watson. 150 pp.1935.